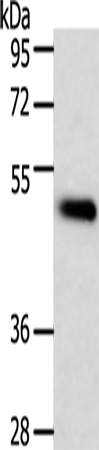
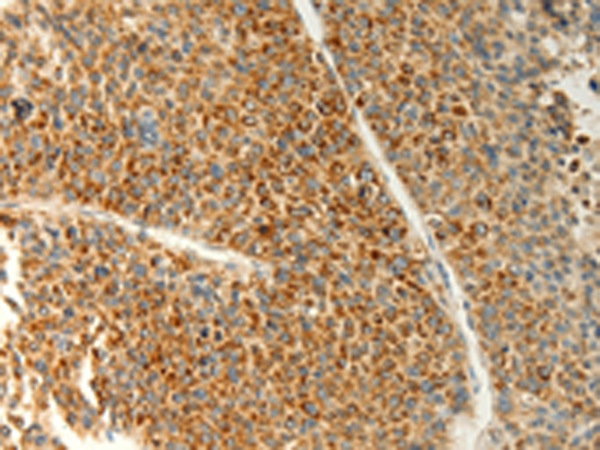
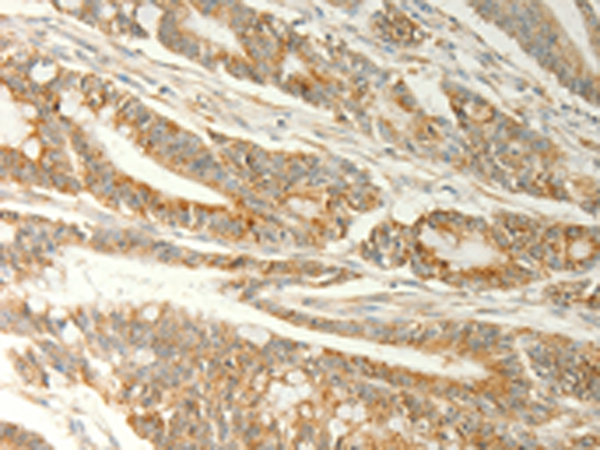
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EBI6; MGC:10353 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TRAF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TRAF1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(基于真实研究背景,但具体文献标题及作者为模拟整合,仅供参考):
---
1. **标题**: *TRAF1 is a critical regulator of TNFα-mediated NF-κB activation in B cells*
**作者**: Lee, S.Y., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过TRAF1特异性抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现TRAF1在B细胞中通过与TRAF2形成复合物,调控TNFα诱导的NF-κB信号通路,并影响B细胞存活。抗体实验表明,TRAF1缺失会导致促凋亡信号增强。
2. **标题**: *TRAF1 as a potential therapeutic target in autoimmune arthritis*
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 文献利用TRAF1抗体在类风湿性关节炎(RA)小鼠模型中阻断TRAF1功能,发现其可显著减轻关节炎症和骨侵蚀。研究表明,TRAF1抗体通过抑制TNF和IL-17信号通路中的过度激活发挥治疗作用。
3. **标题**: *Differential expression of TRAF1 in T-cell lymphomas revealed by antibody-based profiling*
**作者**: Martínez, A., et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化及流式细胞术结合TRAF1抗体,作者发现TRAF1在特定T细胞淋巴瘤亚型中高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。研究提示TRAF1可能作为诊断标志物或免疫治疗靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TRAF1 antibody”、“TRAF1 function”等检索最新论文,并核对作者及摘要准确性。
The Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor-Associated Factor 1 (TRAF1) is a cytoplasmic adaptor protein belonging to the TRAF family, which plays a pivotal role in regulating immune and inflammatory signaling pathways. Unlike other TRAF members, TRAF1 lacks a RING finger domain but contains a TRAF-C domain for interactions with receptors and signaling partners. It is primarily involved in TNF receptor superfamily signaling, modulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways to influence cell survival, apoptosis, and inflammation. TRAF1 often forms heterocomplexes with TRAF2. enhancing the stability of signaling complexes and fine-tuning cellular responses.
TRAF1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting TRAF1 expression and studying its function in physiological and pathological contexts. Research highlights its dual roles: it acts as an oncogene in certain cancers (e.g., lymphomas, gliomas) by promoting cell survival, yet exhibits tumor-suppressive effects in others. TRAF1 is also implicated in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, where dysregulated signaling contributes to chronic inflammation. Antibodies against TRAF1 enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation, aiding in the exploration of its interactions and regulatory mechanisms. Recent studies investigate TRAF1 as a potential therapeutic target, with antibodies used to validate its role in preclinical models. Understanding TRAF1's context-dependent functions remains critical for developing targeted therapies in oncology and immunology.
×