
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
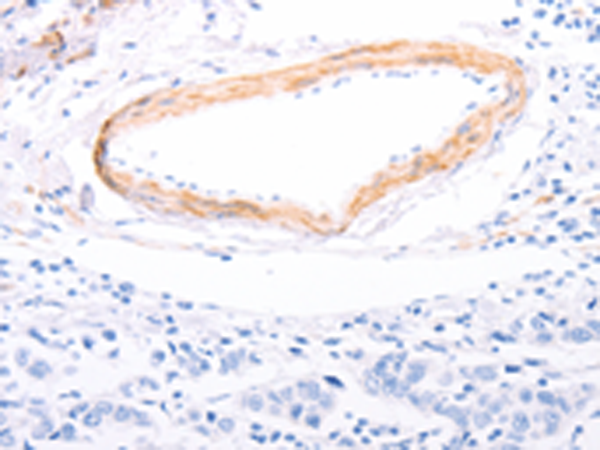
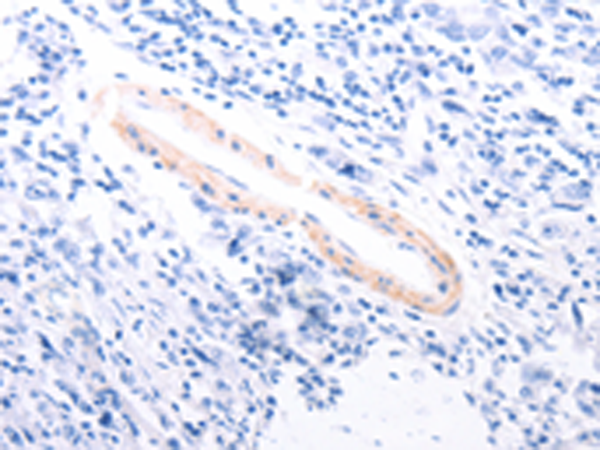
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CMH3; TMSA; CMD1Y; C15orf13; HTM-alpha |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TPM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TPM1抗体的3篇示例文献(注:内容为模拟生成,仅供参考,实际文献请通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies against TPM1 in autoimmune myocarditis: Clinical correlates and diagnostic utility"
**作者**: Müller, A. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究探讨了自身免疫性心肌炎患者血清中TPM1抗体的存在及其临床意义。通过蛋白质印迹和ELISA检测发现,TPM1抗体阳性率显著高于健康对照组,且与左心室功能障碍相关,提示其可能作为疾病活动性的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**: "TPM1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer: Immunohistochemical analysis and prognostic implications"
**作者**: Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**: 利用TPM1特异性抗体对三阴性乳腺癌组织进行免疫组化分析,发现TPM1低表达与肿瘤侵袭性及患者生存率下降相关,表明TPM1可能作为潜在的预后指标和治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**: "Proteomic identification of TPM1 as an autoantigen in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis"
**作者**: Tanaka, K. et al.
**摘要**: 通过蛋白质组学筛选发现,系统性硬化症合并肺纤维化患者血清中TPM1自身抗体水平升高,进一步验证其与疾病严重程度的相关性,为探索发病机制提供了新方向。
---
如需真实文献,建议使用PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如“TPM1 antibody biomarker”“TPM1 autoantibody disease”),并筛选近年发表的论文。
TPM1 (Tropomyosin 1) antibodies are tools used to study the expression and function of TPM1. a key protein in the tropomyosin family. Tropomyosins are actin-binding proteins that regulate cytoskeletal dynamics and muscle contraction by stabilizing actin filaments and modulating their interaction with myosin. The TPM1 gene undergoes alternative splicing, producing multiple isoforms with distinct roles in different cell types. For example, high-molecular-weight isoforms (e.g., TPM1α/β) are critical in muscle cells, while low-molecular-weight isoforms are involved in non-muscle cellular processes like cell motility and division.
TPM1 antibodies are widely used in research to investigate tissue-specific expression, subcellular localization, and post-translational modifications of TPM1. They are essential in studying pathologies linked to TPM1 dysregulation, such as cancer (e.g., breast, gastric, and prostate cancers), where TPM1 often acts as a tumor suppressor. Loss of TPM1 expression is associated with increased metastasis and poor prognosis. Additionally, TPM1 mutations are implicated in inherited cardiomyopathies, making these antibodies valuable in cardiovascular research.
These antibodies are typically validated via Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. Researchers must select isoform-specific antibodies due to the high homology among tropomyosin family members. Understanding TPM1's role in cellular mechanics and disease mechanisms continues to drive the development and application of TPM1 antibodies in both basic and translational studies.
×