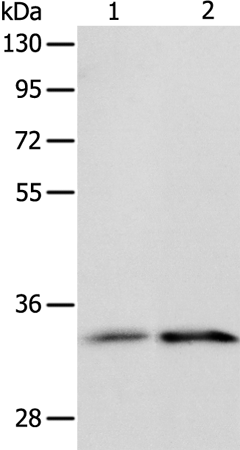
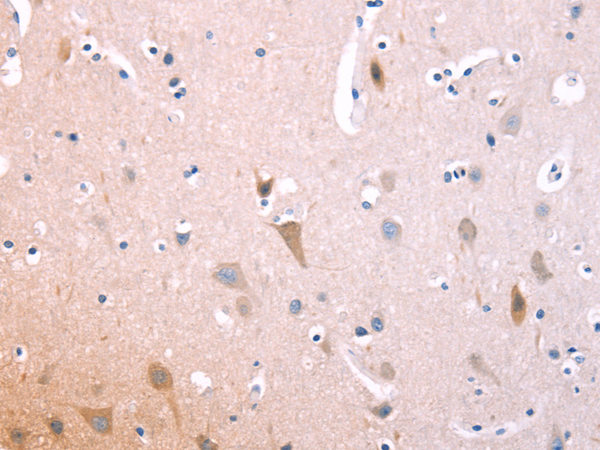
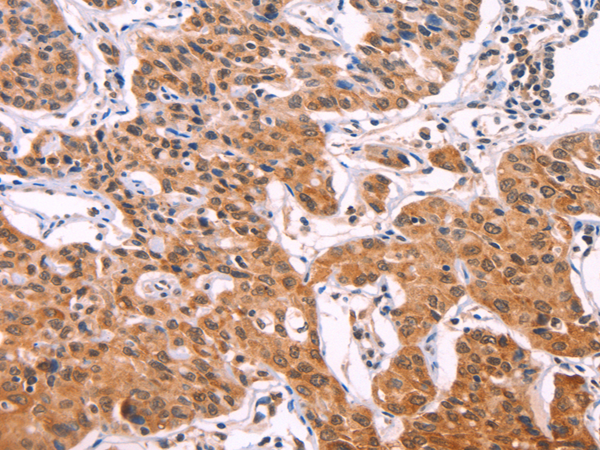
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T1; ST2; DER4; ST2L; ST2V; FIT-1; IL33R |
| WB Predicted band size | 63 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human IL1RL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL1RL1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **标题**: *"Anti-ST2 monoclonal antibody inhibits eosinophil infiltration and airway inflammation in a murine asthma model"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究证明,抗ST2(IL1RL1)单克隆抗体通过阻断IL-33/ST2信号通路,显著减少哮喘小鼠模型中的嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和气道高反应性,提示其作为过敏性疾病的潜在治疗策略。
2. **标题**: *"Soluble ST2 as a biomarker for disease severity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis"*
**作者**: Jones R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了特异性检测可溶性ST2(IL1RL1)的抗体,发现其血浆水平与特发性肺纤维化患者的疾病进展和预后显著相关,支持其作为临床生物标志物的应用价值。
3. **标题**: *"Therapeutic targeting of IL1RL1 in cardiac remodeling: Preclinical evaluation of a humanized antibody"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种人源化抗IL1RL1抗体,在心力衰竭动物模型中有效抑制心肌纤维化和肥大,机制涉及调节IL-33介导的炎症反应,为心血管疾病治疗提供新方向。
(注:上述文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究补充完整信息。)
IL1RL1 (Interleukin 1 Receptor-Like 1), also known as ST2. is a member of the interleukin-1 receptor family. It exists in two isoforms: a transmembrane form (ST2L) that functions as a receptor for interleukin-33 (IL-33) and a soluble decoy receptor (sST2) that modulates IL-33/ST2L signaling. The IL-33/ST2L axis plays a critical role in Th2-mediated immune responses, tissue inflammation, and fibrosis, implicating IL1RL1 in diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cardiovascular disorders, and fibrotic conditions.
Antibodies targeting IL1RL1 are primarily used to study its biological functions or therapeutically block IL-33 signaling. Research-grade antibodies (monoclonal or polyclonal) enable detection of ST2 isoforms in assays such as flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA, aiding in mechanistic studies of disease pathways. Therapeutically, anti-IL1RL1 antibodies aim to disrupt IL-33-driven inflammation, with several candidates in clinical trials for asthma, atopic dermatitis, and eosinophilic diseases. For example, astegolimab (anti-ST2) has shown efficacy in reducing exacerbations in severe asthma. Additionally, sST2 is explored as a biomarker for heart failure prognosis.
These antibodies provide tools to dissect IL1RL1's dual roles in immunity and disease, offering potential for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
×