| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
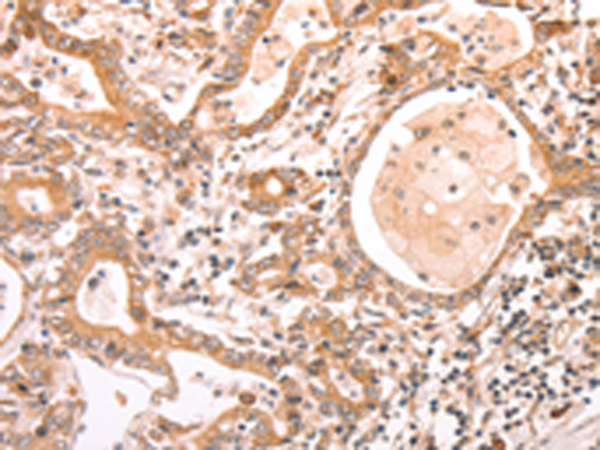
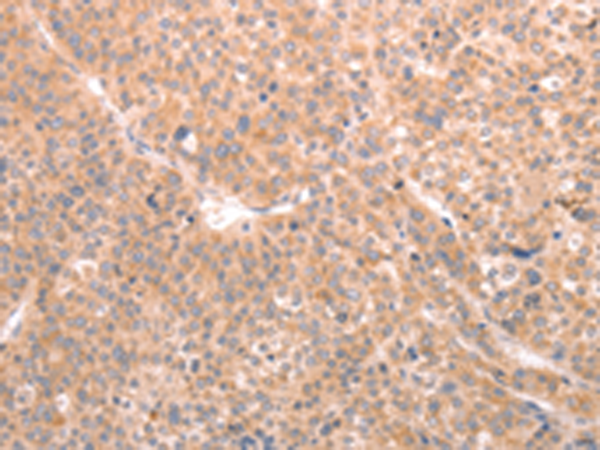
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABC27; ABC50 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ABCF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ABCF1抗体的示例性参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献请通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**: *ABCF1 regulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory response by promoting cytokine production*
**作者**: Lee, J. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过使用ABCF1特异性抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现ABCF1通过增强TLR4信号通路的激活,促进巨噬细胞中IL-6和TNF-α的分泌,提示其在炎症反应中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *ABCF1 as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer: An immunohistochemical study*
**作者**: Smith, R. et al.
**摘要**: 利用ABCF1抗体对乳腺癌组织样本进行免疫组化检测,发现ABCF1的高表达与肿瘤转移和患者生存率降低显著相关,表明其可能作为潜在的预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *Structural insights into ABCF1 ATPase activity using monoclonal antibody-based epitope mapping*
**作者**: Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 通过开发针对ABCF1的单克隆抗体,研究其ATP结合结构域的构象变化,揭示了ABCF1在ATP水解中的分子机制及与抗生素耐药性的关联。
4. **文献名称**: *ABCF1 modulates antiviral immunity via RIG-I signaling pathway*
**作者**: Tanaka, M. et al.
**摘要**: 采用ABCF1抗体敲低细胞内的ABCF1蛋白,证明其通过调控RIG-I介导的干扰素产生,参与宿主抗病毒免疫应答,为病毒感染治疗提供新靶点。
**建议**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以关键词“ABCF1 antibody”或“ABCF1 function”检索最新研究。
The ABCF1 antibody targets the ATP-binding cassette subfamily F member 1 (ABCF1), a ubiquitously expressed protein belonging to the ABC transporter superfamily. Unlike canonical ABC transporters, ABCF1 lacks transmembrane domains, suggesting non-canonical roles in cellular processes. It is implicated in translational regulation, ribosome homeostasis, and immune response modulation. Structurally, ABCF1 contains two nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) critical for ATP hydrolysis, though its exact molecular mechanisms remain under investigation.
ABCF1 is linked to innate immunity, particularly in regulating inflammatory signaling pathways like NF-κB and interferon responses. Studies highlight its interaction with viral RNAs or host stress granules, positioning it as a mediator of antiviral defenses. Dysregulation of ABCF1 has been associated with autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) and cancers, where its overexpression may influence drug resistance or tumor progression.
Antibodies against ABCF1 are widely used in research to detect protein expression via Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. They also facilitate functional studies, such as exploring ABCF1's role in ribosome-associated quality control or immune signaling cascades. Commercial antibodies are often validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, with epitopes typically targeting conserved regions of the N-terminal or NBD domains. Recent applications include investigating ABCF1 as a potential biomarker in autoimmune diagnostics or as a therapeutic target in oncology.
×