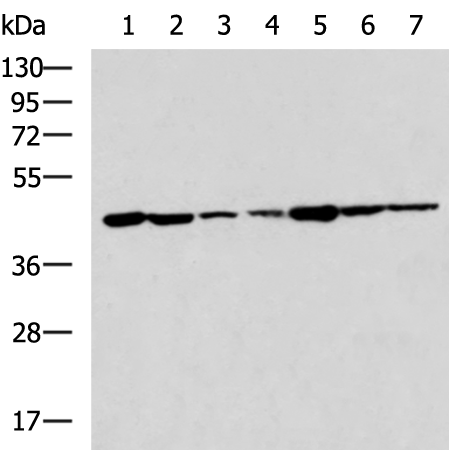
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
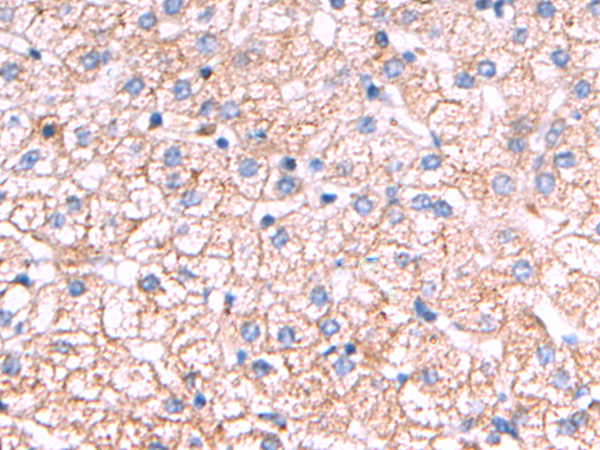
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GA; AGU; ASRG |
| WB Predicted band size | 37 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human AGA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AGA抗体(假设为抗谷氨酸脱羧酶抗体,GAD抗体)的3篇经典文献及摘要概括,以及1篇关于抗麦胶蛋白抗体(Anti-Gliadin Antibodies)的补充文献:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Identification of the 64K Autoantigen in Type 1 Diabetes as the GABA-Synthesizing Enzyme Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase*
**作者**:Baekkeskov, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次证实1型糖尿病中的64K自身抗原为谷氨酸脱羧酶(GAD),揭示了GAD抗体与胰岛β细胞自身免疫损伤的关联,为1型糖尿病的自身免疫机制提供了关键证据。
2. **文献名称**:*GAD65 Autoantibodies in Stiff-Person Syndrome and Type 1 Diabetes*
**作者**:Solimena, M., et al.
**摘要**:研究发现GAD65抗体不仅存在于1型糖尿病患者中,还与僵人综合征(SPS)密切相关,表明GAD抗体可能通过干扰中枢神经系统的GABA能信号传导导致神经功能障碍。
3. **文献名称**:*High-Throughput Radiobinding Assay for Measuring GAD65 Autoantibodies in Diabetes*
**作者**:Lernmark, Å., et al.
**摘要**:该文献开发了一种高效的放射性配体结合检测法,用于精准量化血清中的GAD65抗体水平,推动了1型糖尿病及潜在自身免疫疾病的早期诊断和监测。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-Gliadin Antibodies in Celiac Disease: Diagnostic Significance and Clinical Applications*
**作者**:Volta, U., et al.
**摘要**:探讨抗麦胶蛋白抗体(AGA)在乳糜泻筛查中的敏感性和特异性,指出其在儿童及非典型病例中的诊断价值,同时强调需结合组织学检查确诊。
---
**注**:若用户特指其他类型AGA抗体(如抗麦胶蛋白抗体),建议进一步明确缩写定义以提供更精准的文献。
Anti-gliadin antibodies (AGA) are immunoglobulin (Ig) responses primarily targeting gliadin, a major protein component of gluten found in wheat, barley, and rye. First identified in the 1980s, AGA testing (IgA and IgG subtypes) was initially used as a serological marker for celiac disease (CD), an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed individuals. AGA production reflects immune reactivity to gliadin peptides, which are resistant to digestion and may trigger inflammatory responses in susceptible individuals. However, AGA lacks specificity for CD, as elevated levels are also observed in other conditions, including non-celiac gluten sensitivity, wheat allergy, autoimmune disorders, and intestinal infections.
With advancements in diagnostics, AGA has been largely replaced by more specific markers like tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and endomysial antibodies (EMA). Nevertheless, AGA retains relevance in certain clinical contexts. IgG-AGA is occasionally used to evaluate CD in IgA-deficient patients, while IgA-AGA may assist in pediatric screening due to its early appearance. Research also explores AGA's role in understanding gluten-related immune pathways and extraintestinal manifestations. Despite its limitations, AGA remains a historical cornerstone in the study of gluten-associated disorders, bridging early insights to modern diagnostic frameworks.
×