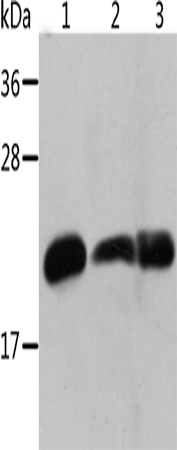
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
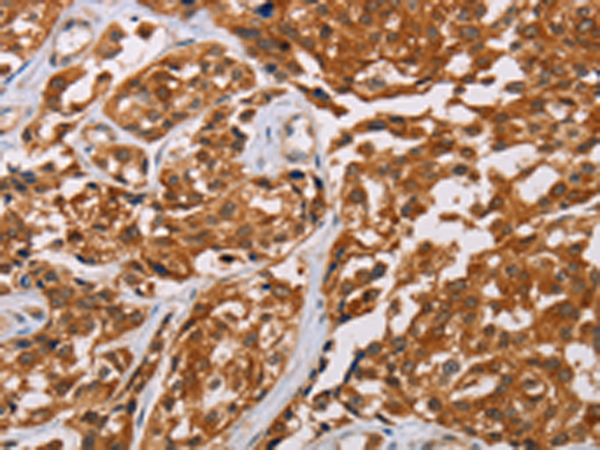
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CRYA2; CTPP2; HSPB5; CMD1II |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CRYAB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CRYAB(αB-crystallin)抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **"αB-crystallin regulates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiac myocytes via modulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation"**
*作者:Morrison et al.*
摘要:研究通过CRYAB抗体检测,发现αB-crystallin通过调节ERK1/2磷酸化通路,抑制心肌细胞在氧化应激下的凋亡,提示其在心脏缺血再灌注损伤中的保护作用。
---
2. **"CRYAB expression in glioblastoma correlates with tumor progression and survival"**
*作者:Wang et al.*
摘要:利用CRYAB抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现胶质母细胞瘤中CRYAB的高表达与肿瘤恶性程度升高及患者总生存期缩短显著相关,表明其可作为潜在预后标志物。
---
3. **"Alpha B-crystallin interacts with mutant SOD1 to mitigate neurotoxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis"**
*作者:Vleminckx et al.*
摘要:通过CRYAB抗体共沉淀实验,证实αB-crystallin与突变SOD1蛋白结合,减少运动神经元内异常蛋白聚集,延缓肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)模型中的神经退行性病变。
---
4. **"CRYAB mutation causes autosomal dominant congenital cataract by altering protein aggregation dynamics"**
*作者:Shi et al.*
摘要:采用CRYAB特异性抗体分析晶状体组织,发现CRYAB基因突变导致蛋白异常聚集,破坏晶状体透明度,阐明了其遗传性白内障的分子机制。
---
这些研究展示了CRYAB抗体在心血管疾病、癌症、神经退行性疾病及眼科疾病中的广泛应用,涵盖机制探索与临床关联分析。
CRYAB (αB-crystallin) is a small heat shock protein (sHSP) belonging to the crystallin family, initially identified as a structural component of the eye lens. It functions as a molecular chaperone, preventing protein aggregation under stress conditions like heat, oxidative stress, or ischemia by stabilizing partially unfolded proteins. Beyond the lens, CRYAB is widely expressed in non-ocular tissues, including cardiac and skeletal muscles, brain, and kidneys, where it plays critical roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis, apoptosis regulation, and cytoskeletal integrity.
CRYAB has been implicated in various diseases. Mutations in the CRYAB gene are linked to cataracts and myofibrillar myopathies. Its dysregulation is associated with neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease), cardiovascular diseases, and cancers. In oncology, CRYAB overexpression in tumors may promote metastasis, chemoresistance, and immune evasion, making it a potential therapeutic target or biomarker.
CRYAB antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying CRYAB expression in research and diagnostics. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study its localization, expression patterns, and interactions in disease models. Commercial CRYAB antibodies vary in host species, clonality, and epitope specificity, requiring rigorous validation for experimental reproducibility. Their applications extend to exploring CRYAB's roles in cellular stress responses, protein quality control, and disease mechanisms, contributing to therapeutic development and diagnostic advancements.
×