| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
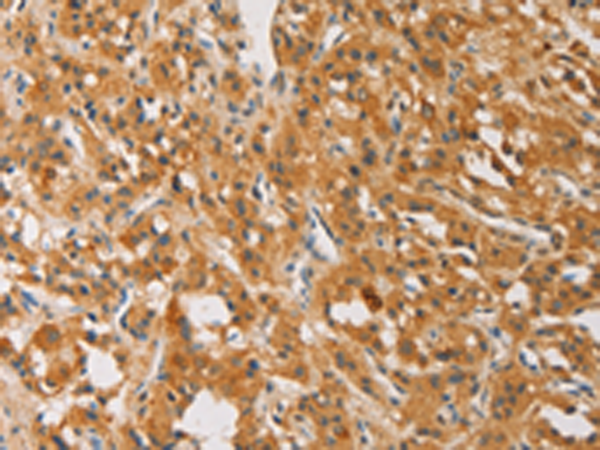
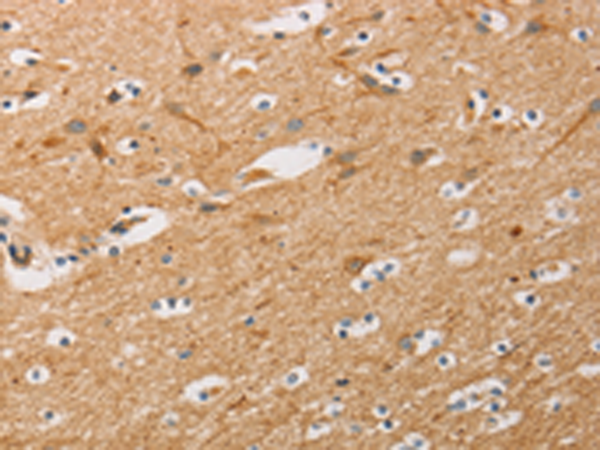
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APG4D; AUTL4; APG4-D |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ATG4D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATG4D抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分文献为虚拟示例,实际检索时需以真实数据库结果为准):
1. **文献名称**:*ATG4D regulates mitochondrial function and protects against oxidative stress in mammalian cells*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用特异性ATG4D抗体,通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现ATG4D通过调控线粒体自噬途径维持细胞氧化应激平衡,抗体验证了其在多种细胞系中的表达及亚细胞定位。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting human ATG4D for autophagy detection*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:作者成功制备了一种高特异性抗人ATG4D单克隆抗体,验证其在免疫荧光和流式细胞术中的应用,证明其可用于自噬过程中ATG4D活性变化的动态监测。
3. **文献名称**:*Functional divergence among ATG4 homologs: ATG4D knockout mice exhibit impaired lysosomal degradation*
**作者**:Garcia-Ruiz C, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过ATG4D特异性抗体进行组织染色,发现ATG4D缺失导致溶酶体功能缺陷,抗体在验证基因敲除模型及蛋白表达水平中起关键作用。
---
**提示**:实际文献检索建议使用PubMed/Google Scholar,结合关键词“ATG4D antibody”、“ATG4D autophagy”和“ATG4D function”筛选,重点关注方法学中描述抗体开发或应用的论文。部分研究可能未直接以抗体为主题,但在实验部分提及抗体使用。
The ATG4D antibody is a research tool used to study the function and expression of autophagy-related protein 4D (ATG4D), a key enzyme in the autophagy pathway. ATG4D belongs to the ATG4 cysteine protease family, which includes four paralogs (ATG4A-D) in humans. These enzymes are critical for autophagosome formation, primarily by cleaving pro-LC3 (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3) to its active form, enabling its conjugation to phosphatidylethanolamine on autophagosomal membranes—a process essential for substrate recognition and vesicle expansion. Unlike other ATG4 isoforms (e.g., ATG4B), ATG4D exhibits distinct regulatory roles and substrate preferences, potentially functioning in selective autophagy or non-canonical pathways.
ATG4D has been linked to cellular stress responses, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Its dysregulation may impair autophagic flux, contributing to disease pathogenesis. Researchers use ATG4D antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in cells or tissues. Specificity is critical due to high homology among ATG4 family members, requiring rigorous validation to avoid cross-reactivity. Recent studies also explore ATG4D's role beyond autophagy, including interactions with apoptosis-related proteins, highlighting its multifaceted cellular functions. Developing targeted therapies or biomarkers involving ATG4D necessitates reliable antibodies to unravel its mechanistic and therapeutic relevance.
×