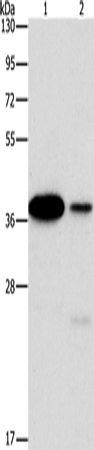
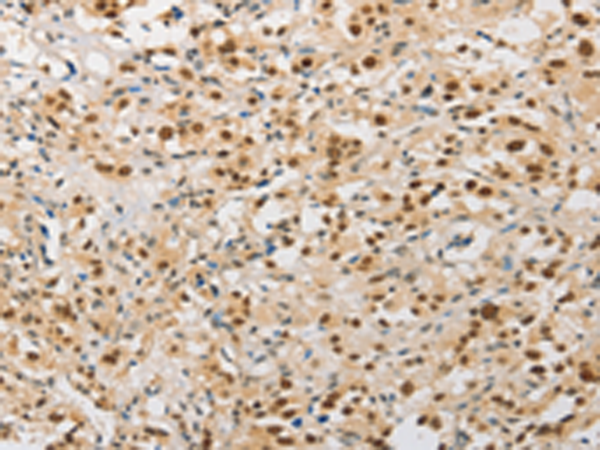
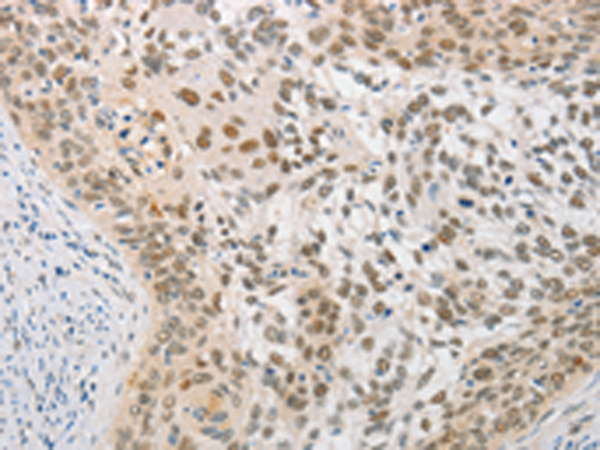
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AOS1; SUA1; UBLE1A; HSPC140 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SAE1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SAE1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"SAE1 promotes human glioma progression through activating AKT signaling"**
- **作者**: Huang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示了SAE1在胶质瘤中的高表达,通过激活AKT信号通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭,提示SAE1可能作为胶质瘤治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **"SUMO-activating enzyme subunit 1 (SAE1) is a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma"**
- **作者**: Liu X, et al.
- **摘要**: 文章通过分析肝癌临床样本,发现SAE1表达与患者不良预后显著相关,其机制可能与调控SUMO化修饰介导的肿瘤转移相关蛋白稳定性有关。
3. **"SAE1 inhibition suppresses triple-negative breast cancer by inducing apoptosis and senescence"**
- **作者**: Zhang L, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究表明,抑制SAE1可通过诱导细胞凋亡和衰老抑制三阴性乳腺癌生长,为靶向SUMO化通路治疗提供了实验依据。
若需更多文献或扩展内容,可进一步说明研究方向(如特定疾病或分子机制)。
**Background of SAE1 Antibody**
SAE1 (SUMO-activating enzyme subunit 1) is a critical component of the SUMOylation pathway, a post-translational modification system that regulates protein localization, stability, and interactions. SAE1 forms a heterodimer with SAE2 to constitute the E1 activating enzyme, which initiates SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) conjugation by ATP-dependent activation of SUMO proteins. This process is essential for diverse cellular functions, including transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, and stress responses.
SAE1 antibodies are valuable tools for studying SUMOylation dynamics. They enable the detection of SAE1 expression levels, localization, and interaction partners in various experimental setups, such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Dysregulation of SAE1 has been implicated in diseases, particularly cancer. Overexpression of SAE1 is observed in malignancies like melanoma and neuroblastoma, correlating with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Conversely, SAE1 inhibition disrupts SUMOylation, leading to impaired oncogenic signaling and apoptosis in cancer cells, highlighting its therapeutic potential.
Research using SAE1 antibodies also explores its role in neurodegenerative disorders and viral infections, where SUMOylation modulates host-pathogen interactions. These antibodies aid in validating SAE1 as a biomarker or drug target in preclinical models. Overall, SAE1 antibodies are pivotal in dissecting the molecular mechanisms of SUMOylation and advancing therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway.
×