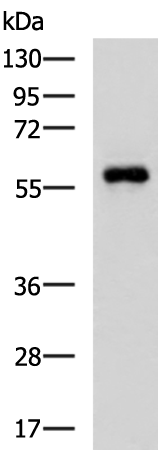
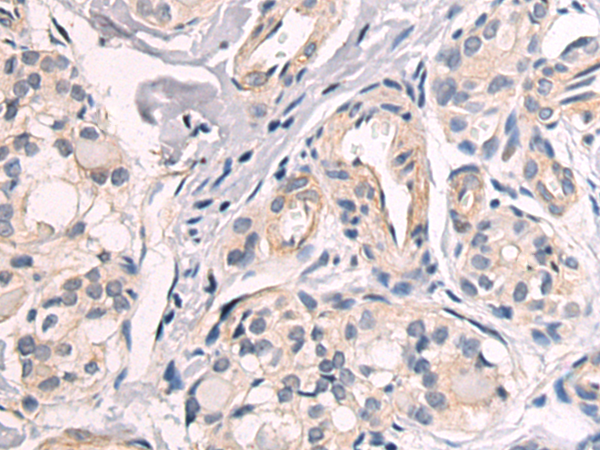
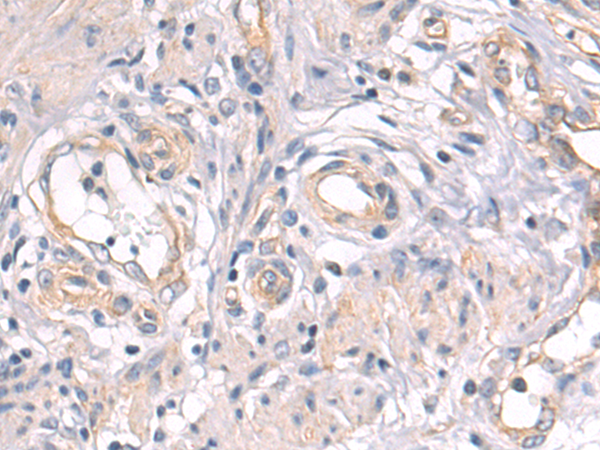
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DA41; DSK2; UBQN; XDRP1; PLIC-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human UBQLN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于UBQLN1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *UBQLN1 interacts with APOE to modulate Aβ uptake and degradation in astrocytes*
**作者**: Hiyama H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用UBQLN1特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀技术揭示UBQLN1与载脂蛋白E(APOE)的相互作用,发现其在阿尔茨海默病中调控星形胶质细胞对β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)的清除能力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Ubiquilin-1 regulates autophagy in α-synucleinopathy models*
**作者**: Lim Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用UBQLN1抗体),证实UBQLN1通过调控自噬途径影响α-突触核蛋白的聚集,为帕金森病病理机制提供新见解。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Loss of UBQLN1 contributes to neurodegeneration through impaired proteostasis*
**作者**: Wu JJ, et al.
**摘要**: 使用UBQLN1敲除小鼠模型和抗体标记技术,发现UBQLN1缺失导致泛素-蛋白酶体系统功能障碍,加剧tau蛋白异常聚集,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的保护作用。
---
如需更多文献或具体应用场景(如抗体品牌/实验方法),可进一步补充说明。
UBQLN1 (ubiquilin-1) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family, primarily involved in regulating protein degradation pathways, including the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. It acts as a molecular chaperone, facilitating the recognition and transport of polyubiquitinated substrates to proteasomes for degradation. UBQLN1 contains an N-terminal ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain for proteasomal interaction and a C-terminal ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain for binding ubiquitinated targets, enabling its critical role in maintaining protein homeostasis. Dysregulation of UBQLN1 has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where protein aggregation is a hallmark.
Antibodies targeting UBQLN1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in cellular and disease models. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect UBQLN1 levels in tissues or cultured cells. Such antibodies help investigate UBQLN1's involvement in stress responses, DNA repair, and autophagy-lysosomal pathways. Commercial UBQLN1 antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, validated for specificity against conserved epitopes across species. Researchers also utilize these antibodies to explore UBQLN1's interactions with disease-associated proteins, such as amyloid-β or tau, providing insights into its potential therapeutic or diagnostic relevance in neurodegeneration and cancer.
×