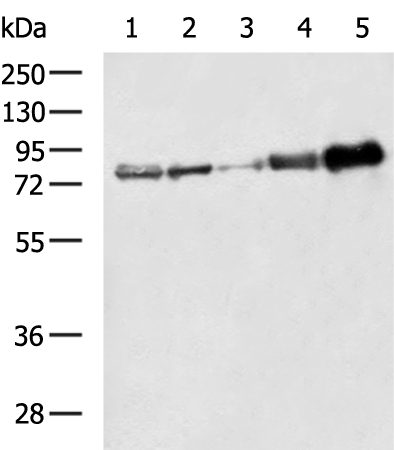
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
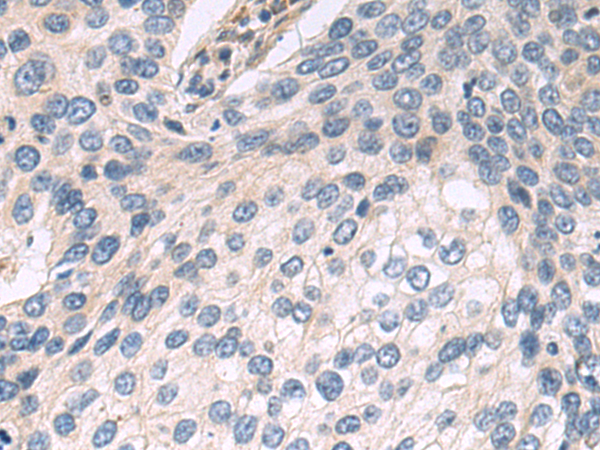
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACS4; FACL4; LACS4; MRX63; MRX68; XLID63 |
| WB Predicted band size | 79 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ACSL4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于ACSL4抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition*
**作者**:Doll, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示ACSL4通过调节细胞膜磷脂的组成调控铁死亡敏感性,并开发特异性ACSL4抗体用于检测其在多种癌细胞中的表达水平,为铁死亡相关治疗提供分子标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis*
**作者**:Kagan, V.E. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ACSL4抗体验证ACSL4在脂质过氧化中的作用,发现其通过催化多不饱和脂肪酸生成促进铁死亡,为神经退行性疾病和癌症治疗提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*ACSL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via c-Myc stability mediated by ERK/FBW7/c-Myc axis*
**作者**:Yuan, B. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用ACSL4抗体)证实ACSL4在肝癌中高表达,并揭示其通过调控c-Myc蛋白稳定性促进肿瘤生长,提示ACSL4可作为肝癌预后标志物。
4. **文献名称**:*Targeting ACSL4 in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities*
**作者**:Tang, D. & Battaglia, A.M.R.
**摘要**:综述ACSL4在肿瘤代谢重编程和铁死亡中的双重作用,强调ACSL4抗体在临床前模型中的诊断和治疗应用潜力,特别是针对三阴性乳腺癌和耐药性肿瘤。
注:以上文献为近年代表性研究,涉及ACSL4抗体的应用场景包括铁死亡机制、癌症标志物检测及治疗靶点验证。
ACSL4 (Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4) is an enzyme critical in lipid metabolism, catalyzing the activation of long-chain fatty acids into acyl-CoA esters. These esters serve as substrates for lipid biosynthesis, energy production, and membrane remodeling. ACSL4 exhibits specificity for polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as arachidonic acid, and is implicated in regulating lipid composition in cellular membranes. Dysregulation of ACSL4 has been linked to multiple pathological conditions. Notably, it plays a key role in ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death driven by lipid peroxidation, where ACSL4-mediated PUFA incorporation into membranes promotes susceptibility to oxidative damage. This connection positions ACSL4 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in cancers resistant to apoptosis, including triple-negative breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma.
ACSL4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research on its role in disease mechanisms. Mutations in the ACSL4 gene are also associated with X-linked intellectual disability and developmental disorders, highlighting its importance in neuronal function. Furthermore, ACSL4 antibodies contribute to exploring sex-specific disease patterns, as the gene resides on the X chromosome. Overall, ACSL4 antibodies are pivotal in elucidating metabolic pathways, disease pathogenesis, and potential therapeutic strategies targeting lipid metabolism and cell death pathways.
×