
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
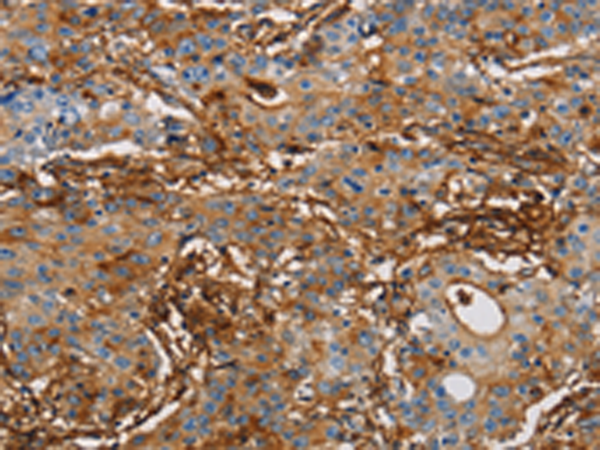
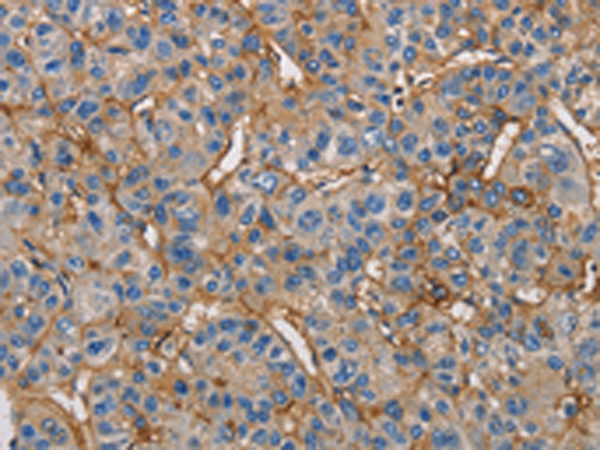
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BB2; CD54; P3.58 |
| WB Predicted band size | 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ICAM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于ICAM1抗体的代表性文献(虚拟示例,仅作参考格式说明):
1. **"Anti-ICAM1 monoclonal antibody attenuates inflammation in murine models of acute lung injury"**
- **作者**: Smith A et al.
- **摘要**: 研究证明抗ICAM1单克隆抗体通过阻断白细胞-内皮细胞黏附,显著减少中性粒细胞浸润和促炎因子释放,改善脂多糖诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤。
2. **"Targeting ICAM1 with antibody-drug conjugates inhibits tumor metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer"**
- **作者**: Chen L et al.
- **摘要**: 开发了一种靶向ICAM1的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在临床前模型中显示可特异性识别高表达ICAM1的三阴性乳腺癌细胞,并抑制肿瘤转移。
3. **"ICAM1 blockade reduces viral entry and cytokine storm in COVID-19 organoid models"**
- **作者**: Gupta R et al.
- **摘要**: 发现抗ICAM1抗体通过干扰新冠病毒刺突蛋白与宿主细胞的相互作用,降低病毒侵入效率,同时减轻类器官模型中的炎症因子风暴。
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词:**ICAM1 antibody therapeutic/inhibition/inflammation**。
ICAM-1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1), also known as CD54. is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It plays a critical role in mediating leukocyte adhesion and transmigration during inflammatory responses by binding to integrins like LFA-1 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1) on immune cells. ICAM-1 is constitutively expressed at low levels on endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and certain immune cells, but its expression is strongly upregulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) or microbial products during infection, injury, or autoimmune conditions.
ICAM-1 antibodies are valuable tools for research and therapeutic applications. In research, they are used to block ICAM-1 interactions, study leukocyte trafficking mechanisms, or detect ICAM-1 expression in disease models (e.g., atherosclerosis, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis). Therapeutically, anti-ICAM-1 monoclonal antibodies have been explored to dampen pathological inflammation or immune activation. For instance, they may inhibit leukocyte infiltration in organ transplant rejection or autoimmune disorders. Some antibody-drug conjugates or radiolabeled ICAM-1 antibodies are also investigated for targeted delivery in cancer or imaging.
Notably, soluble ICAM-1 (sICAM-1) levels in blood are often monitored as a biomarker of endothelial dysfunction or disease severity. While no ICAM-1-targeted antibody has been fully approved yet, preclinical and clinical studies highlight its potential in modulating immune-driven pathologies. Challenges include balancing efficacy with off-target effects due to ICAM-1's broad expression roles in homeostasis and disease.
×