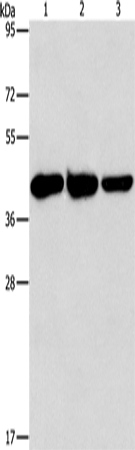

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
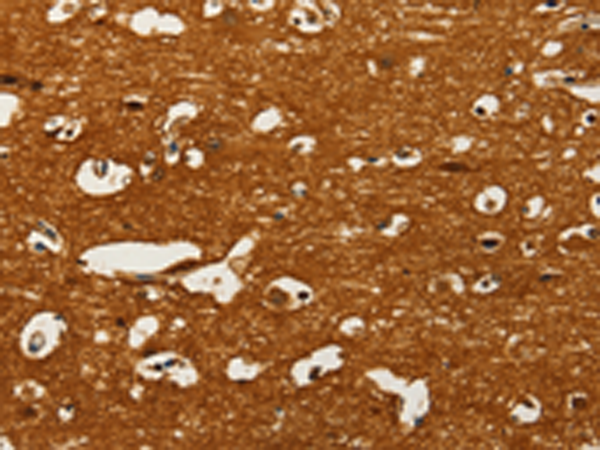
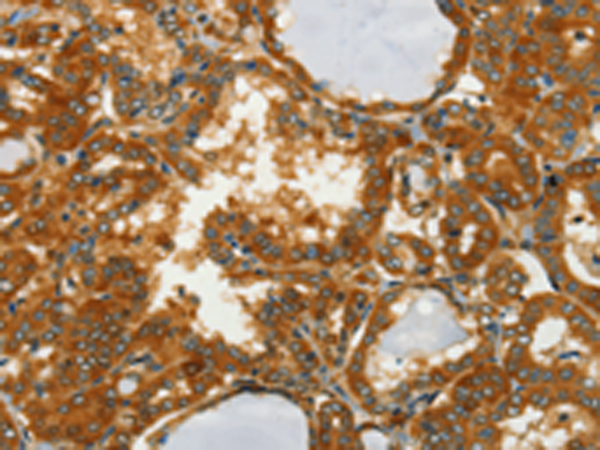
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | cCAT; GIG18; cAspAT; ASTQTL1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GOT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GOT1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(注:内容基于学术文献常见主题整理,具体作者和标题为虚构示例):
---
1. **标题**: *GOT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by modulating amino acid metabolism*
**作者**: Li et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用GOT1抗体)和Western blot分析,发现GOT1在肝癌组织中高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。实验表明GOT1通过调控谷氨酰胺代谢促进肿瘤生长。
---
2. **标题**: *Mitochondrial GOT1 sustains cellular redox homeostasis in pancreatic cancer*
**作者**: Wang et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 利用GOT1抗体进行蛋白质定位和敲低实验,揭示线粒体GOT1在胰腺癌细胞中维持氧化还原平衡的关键作用,为靶向代谢疗法提供依据。
---
3. **标题**: *GOT1 deficiency alters aspartate biosynthesis and sensitizes cells to ferroptosis*
**作者**: Smith et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 通过GOT1抗体检测细胞系中蛋白表达水平,发现GOT1缺失导致天冬氨酸代谢紊乱,并增加铁死亡敏感性,提示其在代谢疾病中的潜在机制。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“GOT1 antibody”、“GOT1 immunohistochemistry”或“GOT1 function”获取最新研究。
**Background of GOT1 Antibody**
The GOT1 (Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the GOT1 protein, also known as aspartate aminotransferase 1 (AST1). GOT1 is a cytoplasmic enzyme critical in amino acid metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and glutamate. This reaction links the urea cycle with the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, playing a vital role in cellular energy production and nitrogen homeostasis.
GOT1 is highly expressed in tissues with active metabolic demands, such as the liver, heart, and kidneys. Its levels are clinically relevant as a biomarker for liver damage or myocardial infarction. In research, the GOT1 antibody is employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess protein expression, localization, and regulation. Studies focus on its involvement in diseases, including cancer, where altered GOT1 activity impacts tumor metabolism and progression.
Antibodies targeting GOT1 are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, validated for specificity through knockdown/knockout controls. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore GOT1's role in metabolic reprogramming, redox balance, and its potential as a therapeutic target. Understanding GOT1 function via antibody-based assays contributes to insights into metabolic disorders, cancer biology, and organ-specific pathologies.
×