

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
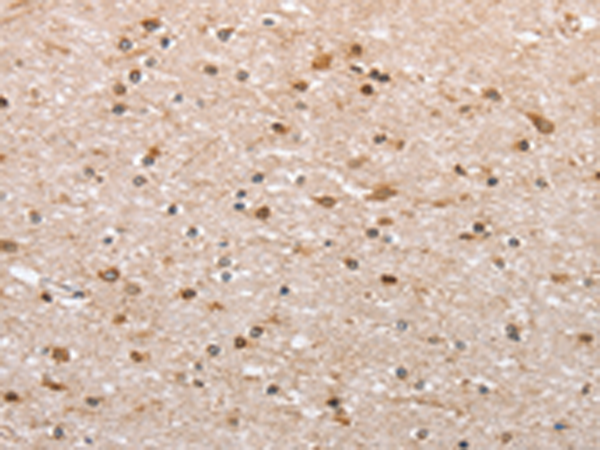
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CNX; P90; IP90 |
| WB Predicted band size | 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CANX |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CANX(Calnexin)抗体相关的文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:Calnexin: A membrane-bound chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum
**作者**:David B. Williams
**摘要**:该综述总结了Calnexin在内质网中的分子伴侣功能,重点讨论其通过识别新生糖蛋白参与折叠质量控制的作用。文献提及利用特异性CANX抗体证实其与未折叠蛋白的相互作用,并阐述其在ERAD(内质网相关降解)通路中的调控机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:Calnexin deficiency leads to dysmyelination in mice
**作者**:Jia N. Wang et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过敲除小鼠模型发现Calnexin缺失导致髓鞘形成异常。Western blot和免疫组化使用CANX抗体显示,Calnexin在少突胶质细胞中高表达,其缺失引发内质网应激,进而影响髓鞘相关蛋白(如MAG)的正确折叠和运输。
---
3. **文献名称**:Interaction of calnexin with hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins
**作者**:Claire Choukhi et al.
**摘要**:文章利用免疫共沉淀和CANX抗体研究发现,丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)的包膜糖蛋白E1/E2在宿主细胞中依赖Calnexin进行折叠。实验证实,抑制Calnexin功能或使用抗体阻断其活性会显著降低病毒颗粒的组装效率。
---
4. **文献名称**:Calnexin is required for tumor cell apoptosis via EGFR/MAPK signaling
**作者**:Yuki Nakamura et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过siRNA沉默及CANX抗体检测发现,Calnexin通过调控EGFR的膜定位影响MAPK信号通路。在肺癌细胞中,Calnexin缺失导致EGFR异常滞留于内质网,从而抑制凋亡并促进化疗耐药性。
---
以上文献涵盖了Calnexin在蛋白质折叠、疾病模型、病毒宿主互作及肿瘤信号通路中的研究,均明确使用CANX抗体进行机制验证。
**Background of CANX Antibodies**
CANX (Calnexin) is a 90 kDa chaperone protein primarily located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. It plays a critical role in the quality control of glycoprotein folding by binding to monoglucosylated N-linked glycans, ensuring proper folding and assembly of nascent proteins. Calnexin also interacts with ERp57. a thiol-oxidoreductase, to facilitate disulfide bond formation. Additionally, it participates in the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway, targeting misfolded proteins for proteasomal degradation.
CANX antibodies are widely used in research to study ER stress, protein folding dynamics, and diseases linked to proteostasis dysfunction, such as neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and cancer. These antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect Calnexin expression, localization, and interactions.
Most CANX antibodies are raised against conserved epitopes, enabling cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat). Validation includes verifying specificity via knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown. Due to its ER retention signal (KDEL-like motif), Calnexin is also used as an ER marker in subcellular localization studies. Researchers must consider potential cross-reactivity with calreticulin, a soluble homolog, when interpreting results.
×