| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
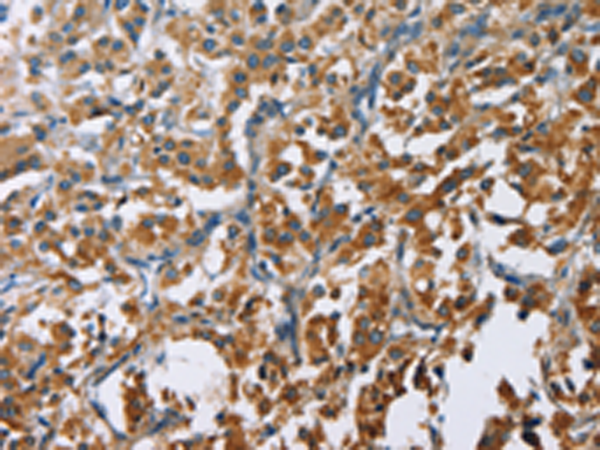
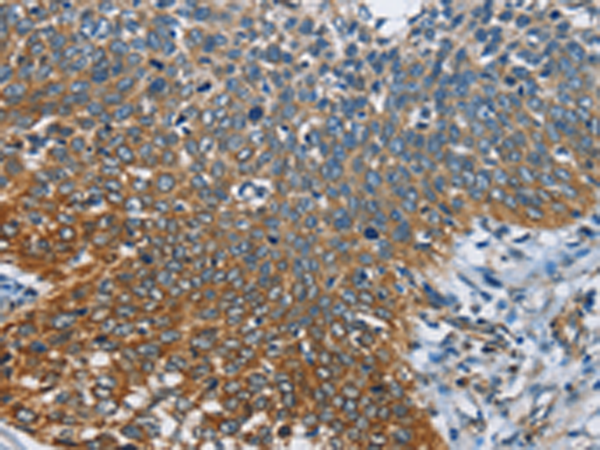
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CANDF2; hCARD9 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CARD9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CARD9抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*CARD9 Signaling in Innate Immunity and Inflammation*
**作者**:Drummond R.A. 等
**摘要**:探讨CARD9在先天免疫反应中的作用,研究利用特异性抗体揭示其介导抗真菌信号通路的机制,发现CARD9缺陷与慢性黏膜念珠菌病相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CARD9 Autoantibodies in Neutrophilic Dermatoses*
**作者**:Hsu C.L. 等
**摘要**:报道在嗜中性皮肤病中检测到抗CARD9自身抗体,提示其可能通过干扰中性粒细胞功能加剧炎症,为疾病诊断提供潜在标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*CARD9 Antibody Blockade Attenuates Colitis in Murine Models*
**作者**:Wang X. 等
**摘要**:通过CARD9中和抗体抑制肠道炎症反应,证明靶向CARD9可减轻实验性结肠炎小鼠的病理损伤,提示治疗炎症性肠病的潜力。
(注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认。)
CARD9 (Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 9) is a pivotal adaptor protein in innate immunity, primarily involved in antifungal defense and inflammatory signaling. Structurally, it contains an N-terminal CARD domain and a coiled-coil domain, enabling interactions with other signaling molecules like BCL10 and MALT1 to form the CARD9-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) complex. This complex activates downstream pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK, triggering cytokine production and immune cell activation. CARD9 is predominantly expressed in myeloid cells (e.g., dendritic cells, macrophages), linking pathogen recognition by receptors (e.g., Dectin-1) to adaptive immune responses.
Research highlights CARD9's critical role in fungal immunity, as mutations in CARD9 are linked to susceptibility to invasive fungal infections (e.g., candidiasis, aspergillosis). Dysregulated CARD9 signaling is also implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-CARD9 antibodies are essential tools for studying these mechanisms, enabling detection of protein expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation. Commercial antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, aiding both basic research and clinical investigations into immune dysregulation. Understanding CARD9 pathways offers potential therapeutic targets for modulating immune responses in infection and chronic inflammation.
×