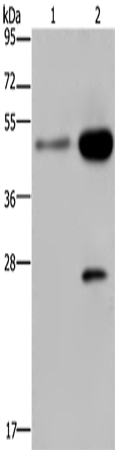
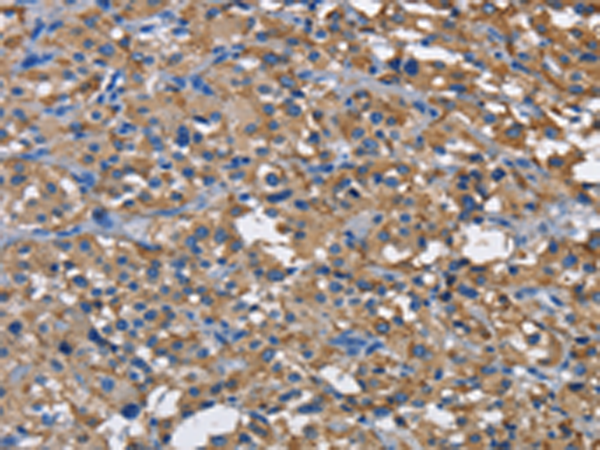
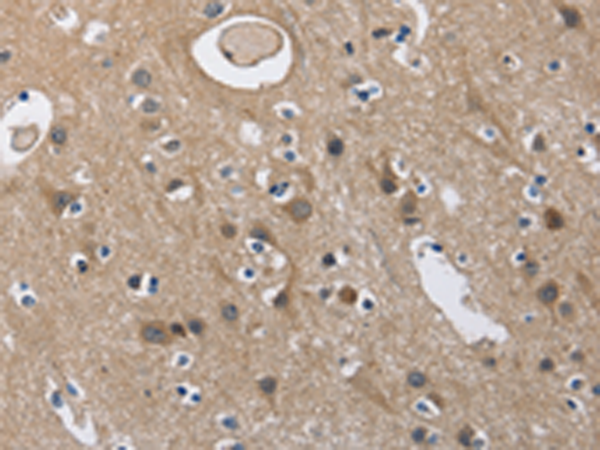
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NK1; BY55; NK28 |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD160 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD160抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*CD160 signaling enhances T-cell responses in inflammation and cancer*
**作者**:Ana Maria Lennon-Duménil 等
**摘要**:研究揭示了CD160在T细胞活化和抗肿瘤免疫中的作用,发现CD160抗体通过增强T细胞受体(TCR)信号通路,促进效应T细胞的增殖和细胞因子分泌,为肿瘤免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD160 with a monoclonal antibody inhibits virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses*
**作者**:Giulia Martinvalet 等
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向CD160的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过阻断CD160与疱疹病毒入侵介导因子(HVEM)的相互作用,抑制病毒特异性CD8+ T细胞的耗竭,为慢性病毒感染治疗提供潜在手段。
3. **文献名称**:*CD160 regulates NK cell-mediated antitumor immunity via interaction with HVEM*
**作者**:Christine Sedlik 等
**摘要**:研究聚焦CD160在自然杀伤(NK)细胞中的功能,发现CD160抗体通过调控HVEM信号通路,增强NK细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤活性,并改善肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制状态。
如需更具体的文献信息,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中以“CD160 antibody”为关键词进一步检索。
×