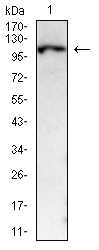
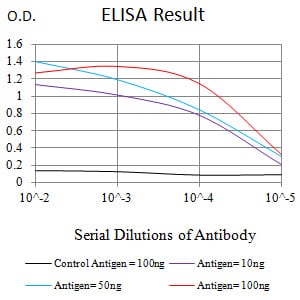
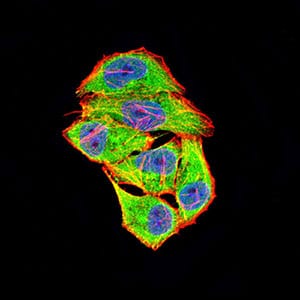
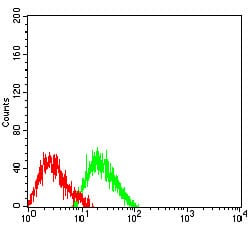
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
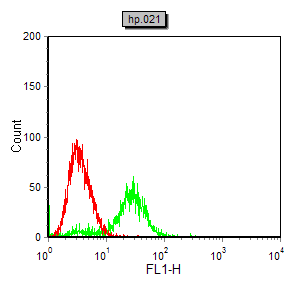
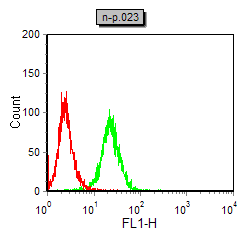
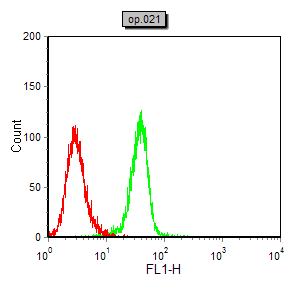
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OI4; EDSCV; EDSARTH2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1278 |
| clone | 4D1A7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 129kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human COL1A2 (AA: 23-79) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD177抗体的3篇代表性文献(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*CD177-mediated neutrophil activation in autoimmune vasculitis*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究CD177抗体在抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体(ANCA)相关血管炎中的作用,发现CD177抗体通过结合中性粒细胞表面抗原,促进炎症反应及组织损伤。
2. **文献名称**:*CD177 as a biomarker for colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**:Zhang L, Wang Y.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析发现,CD177抗体可特异性识别肿瘤微环境中的CD177+中性粒细胞,其高表达与结直肠癌转移和不良预后显著相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a novel anti-CD177 monoclonal antibody for therapeutic targeting*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型人源化CD177抗体的开发,该抗体在体外和小鼠模型中有效抑制中性粒细胞迁移,提示其潜在应用于炎症性疾病治疗。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需查询PubMed或专业数据库获取真实文献。)
CD177. also known as Human Neutrophil Antigen-2a (HNA-2a), is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein predominantly expressed on neutrophils. It belongs to the LY-6 gene superfamily and plays a role in neutrophil migration, activation, and interaction with endothelial cells. CD177 binds to proteinase 3 (PR3), a serine protease, forming membrane complexes implicated in autoimmune disorders like ANCA-associated vasculitis (e.g., granulomatosis with polyangiitis).
CD177 antibodies are critical tools in research and diagnostics. Clinically, they help identify HNA-2a antigens in transfusion medicine to prevent alloimmune neonatal neutropenia or transfusion-related reactions. In research, these antibodies are used to study neutrophil heterogeneity, as CD177+ and CD177− subsets exhibit functional differences in inflammation and immune responses. Additionally, CD177 antibodies aid in exploring its role in diseases, including autoimmune conditions, infections, and cancer. CD177 is overexpressed in certain malignancies (e.g., colorectal cancer), suggesting potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target.
Monoclonal anti-CD177 antibodies are widely employed in flow cytometry, immunoassays, and immunohistochemistry to characterize neutrophil subsets or detect pathological CD177 expression. However, its variable _expression (absent in 3–5% of the population) and unclear regulatory mechanisms highlight the need for further studies. Overall, CD177 antibodies remain pivotal in understanding neutrophil biology and related pathologies.
×