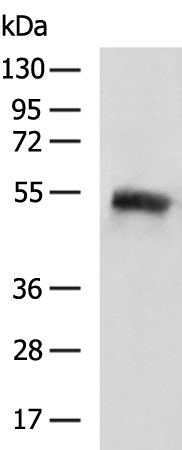
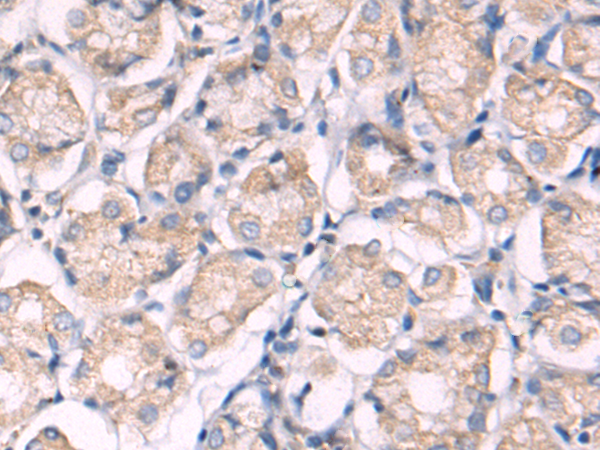
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD329; CDw329; FOAP-9; siglec-9; OBBP-LIKE |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SIGLEC9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **SIGLEC9 抗体**的 3 篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Siglec-9 is an inhibitory receptor on human mast cells in contact allergy*
**作者**: Körner, M. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究发现 Siglec-9 在接触性过敏反应中通过结合唾液酸聚糖抑制肥大细胞活化。抗 Siglec-9 抗体可阻断这一通路,增强肥大细胞的促炎反应,提示其作为炎症性疾病的潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Siglec-9 defines a novel inhibitory checkpoint in cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Wang, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了 Siglec-9 在肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制作用,通过结合肿瘤细胞表面唾液酸配体抑制 T 细胞活性。使用抗 Siglec-9 抗体可解除抑制信号,增强抗肿瘤免疫反应,为癌症免疫治疗提供了新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Targeting Siglec-9 in macrophages for modulation of inflammatory responses*
**作者**: Chen, G.Y. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究表明,Siglec-9 在巨噬细胞中通过调控 TLR 信号通路抑制炎症反应。抗 Siglec-9 抗体可逆转免疫抑制表型,促进促炎细胞因子分泌,提示其在治疗慢性感染或脓毒症中的潜在应用。
---
这些文献展示了 Siglec-9 抗体在免疫调节、肿瘤治疗和炎症疾病中的关键作用。如需全文链接或更多细节,可进一步提供。
SIGLEC9 (sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin 9) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the SIGLEC family of immune-regulatory receptors, primarily expressed on myeloid cells like monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. It recognizes sialic acid-containing glycans on cell surfaces, transmitting inhibitory signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) to modulate immune responses. SIGLEC9 plays a dual role in balancing immune activation and tolerance. In physiological conditions, it helps dampen excessive inflammation by promoting phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine release. However, in pathologies like cancer, chronic inflammation, or sepsis, its overexpression is often exploited by diseased cells to evade immune detection. For instance, tumor cells expressing sialylated ligands engage SIGLEC9 on infiltrating myeloid cells, inducing immunosuppressive phenotypes that facilitate tumor progression.
SIGLEC9 antibodies, either antagonistic or agonistic, are investigational tools and therapeutic candidates. Blocking antibodies aim to disrupt SIGLEC9-mediated immunosuppression in cancer immunotherapy, potentially enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Conversely, agonist antibodies may treat inflammatory disorders by amplifying SIGLEC9’s anti-inflammatory signals. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and understanding context-dependent signaling. Research continues to explore its tissue-specific roles, ligand interactions, and crosstalk with other checkpoint receptors like PD-1/PD-L1.
×