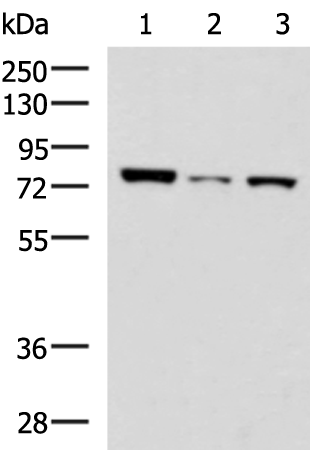
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
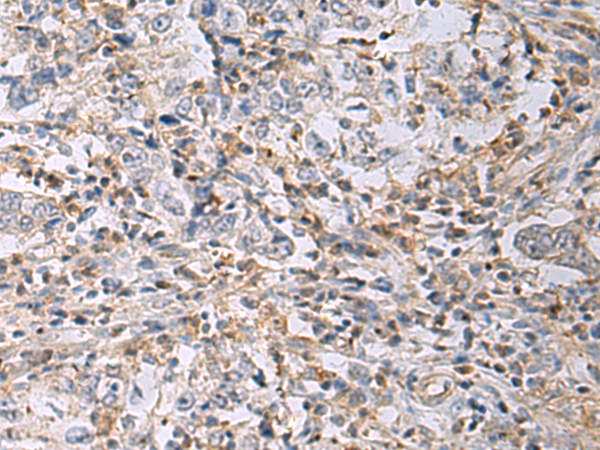
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p67; SIGLEC3; SIGLEC-3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD33 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD33抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin in Acute Myeloid Leukemia*
**作者**:Scott, A. M. 等
**摘要**:该III期临床试验验证了吉妥珠单抗奥佐米星(CD33抗体-化疗药物偶联物)在复发/难治性急性髓系白血病(AML)中的疗效,显示其可延长部分患者生存期,但伴随肝毒性等副作用,提示需优化用药方案。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CD33-directed immunotherapy with lintuzumab in AML*
**作者**:Castaigne, S. 等
**摘要**:研究评估了人源化CD33单抗(Lintuzumab)联合化疗治疗老年AML患者的效果,结果显示总缓解率提升,但未能显著改善长期生存,提示单一靶向CD33可能需与其他疗法联用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Resistance mechanisms to CD33-targeted therapy in leukemia*
**作者**:Naito, K. 等
**摘要**:该研究揭示了AML细胞对CD33抗体药物产生耐药的分子机制,包括抗原内化障碍和药物外排泵激活,为开发逆转耐药策略提供了理论依据。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Novel humanized anti-CD33 antibodies for CAR-T therapy*
**作者**:Dahlen, E. 等
**摘要**:报道了一种新型人源化CD33抗体设计,可增强CAR-T细胞对AML细胞的靶向杀伤活性,并在临床前模型中显著减少肿瘤负荷,为免疫治疗提供新方向。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需核对原文信息。CD33抗体的研究主要集中在AML治疗及耐药机制,近年拓展至CAR-T等新型免疫疗法领域。
CD33. also known as Siglec-3. is a transmembrane receptor protein belonging to the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) family. It is primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts, and plays a role in modulating immune responses through inhibitory signaling. CD33 gained clinical significance as a therapeutic target due to its overexpression in AML cells, making it a marker for antibody-based therapies.
The development of CD33-targeting antibodies began in the 1990s, with gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO) being the first FDA-approved anti-CD33 antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) in 2000. GO combines a humanized anti-CD33 antibody with the cytotoxic agent calicheamicin, designed to selectively deliver chemotherapy to CD33-positive cells. Despite initial enthusiasm, its use was limited by toxicity concerns and variable efficacy, leading to temporary withdrawal from the market before re-approval with refined dosing guidelines.
Research continues to explore improved CD33-targeting strategies, including bispecific antibodies, CAR-T cells, and next-generation ADCs with more stable linkers and potent payloads. Challenges persist due to CD33 heterogeneity in AML populations, antigen modulation upon antibody binding, and on-target/off-tumor effects on healthy myeloid cells. Ongoing studies aim to optimize therapeutic windows and overcome resistance mechanisms, maintaining CD33 as a key focus in myeloid malignancy immunotherapy development.
×