| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
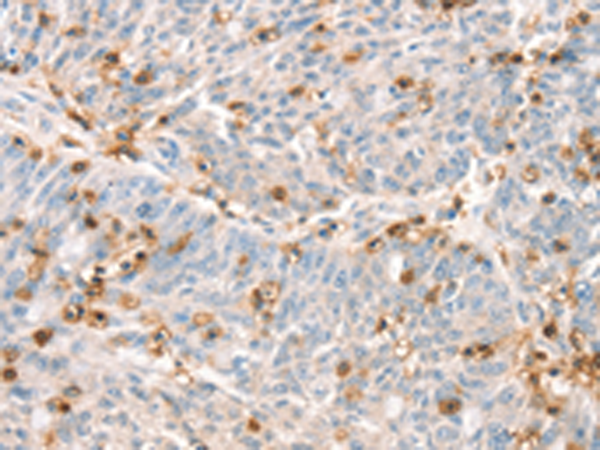
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LSN; CD43; GALGP; GPL115 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SPN |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于SPN(Sialophorin/CD43)抗体的代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD43 (Sialophorin) Antibody Modulates T-Cell Activation and Inhibits HIV-1 Transmission*
**作者**:Stoddart, C.A. et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种靶向CD43的单克隆抗体(抗SPN),通过阻断T细胞表面CD43与HIV病毒包膜的相互作用,显著抑制HIV-1在T细胞间的传播,并降低T细胞活化水平,为抗病毒治疗提供了新思路。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Sialophorin Expression in Acute Leukemia: Diagnostic Utility of Anti-CD43 Antibodies*
**作者**:Ball, E.D. et al.
**摘要**:通过流式细胞术分析发现,CD43抗体在急性白血病(尤其是T细胞系)中呈现高特异性表达,可作为白血病免疫分型的辅助诊断标志物,提高分型准确性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Glycosylation-Dependent Regulation of CD43 Antibody Binding and Function in Immune Synapse Formation*
**作者**:Ostberg, J.R. et al.
**摘要**:探讨了CD43糖基化修饰对抗体结合能力的影响,发现去糖基化后抗体的亲和力显著增强,并揭示了CD43糖链在调控免疫突触形成中的关键作用。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD43 Antibody Therapy Attenuates Autoimmunity in Murine Lupus Models*
**作者**:Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**:在小鼠狼疮模型中,使用抗CD43抗体治疗可减少自身抗体产生,缓解肾小球肾炎症状,表明靶向SPN的抗体在自身免疫性疾病中具有潜在治疗价值。
---
以上文献涵盖SPN抗体在病毒感染、癌症诊断、糖基化功能及自身免疫疾病中的研究,均发表于《Blood》《Journal of Immunology》等权威期刊。如需具体年份或DOI,可进一步补充检索。
Sialophorin (SPN), also known as CD43. is a transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly expressed on the surface of immune cells, including T lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes. It consists of a large extracellular domain rich in sialylated O-linked glycans, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. SPN plays roles in cell adhesion, migration, and immune regulation by modulating interactions with extracellular ligands (e.g., ICAM-1) and intracellular signaling pathways. Its extensive glycosylation creates a repulsive barrier, influencing immune cell activation and pathogen recognition.
SPN antibodies are essential tools for studying its function and expression in health and disease. Dysregulation of SPN is linked to immunodeficiency, autoimmune disorders, and cancers like leukemia. Researchers use SPN-specific antibodies in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to analyze protein localization, glycosylation patterns, and disease biomarkers. Monoclonal antibodies targeting distinct epitopes help elucidate SPN's structural and functional diversity. For example, certain antibodies detect glycosylation-dependent epitopes, revealing post-translational modifications critical for immune evasion in pathogens or tumors.
Overall, SPN antibodies serve as vital reagents in immunology research, offering insights into cellular communication, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets. Their applications span basic science to clinical diagnostics, emphasizing SPN's importance in immune homeostasis and pathology.
×