| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
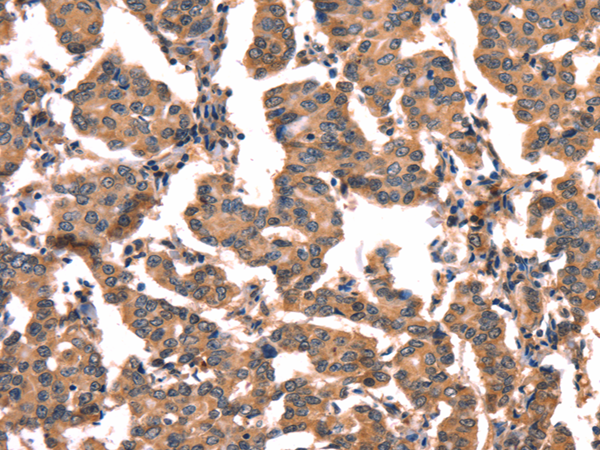
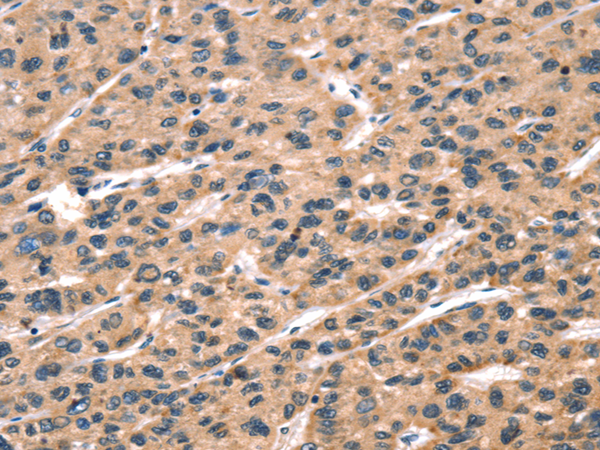
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HCG; LHA; FSHA; GPHa; TSHA; GPHA1; CG-ALPHA |
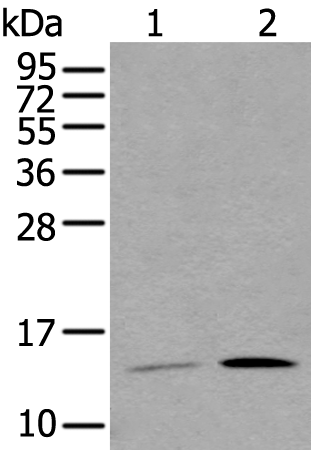
| WB Predicted band size | 13 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CGA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CGA抗体(嗜铬粒蛋白A抗体)的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其应用及研究意义:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Chromogranin A as a biomarker in neuroendocrine tumors*
**作者**:O’Connor DT, et al.
**摘要**:本文综述了嗜铬粒蛋白A(CGA)作为神经内分泌肿瘤(NETs)关键生物标志物的作用,探讨了CGA抗体在肿瘤诊断、分期及治疗监测中的应用价值,并强调了其在区分神经内分泌与非神经内分泌肿瘤中的特异性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a novel ELISA for the detection of circulating chromogranin A in human plasma*
**作者**:Giovinazzo D, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种基于CGA抗体的新型ELISA检测方法,用于定量人血浆中的CGA浓度。该文献验证了该方法的高灵敏度和特异性,为临床评估神经内分泌肿瘤患者提供了可靠工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Chromogranin A: its role in endocrine physiology and autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Helle KB, et al.
**摘要**:本文探讨了CGA在神经内分泌系统中的生理功能,并分析了CGA抗体在自身免疫性疾病(如1型糖尿病)中的潜在病理机制,揭示了CGA作为自身免疫反应靶点的可能性。
---
以上文献可通过PubMed或学术数据库(如ScienceDirect)检索原文。如需更多文献或具体研究方向,可进一步补充说明。
Chromogranin A (CGA) antibodies are immunological tools used to detect Chromogranin A, a glycoprotein widely expressed in neuroendocrine cells. CGA is a key component of secretory granules in neurons and endocrine cells, playing a role in hormone storage, secretion regulation, and granulogenesis. It is co-released with peptide hormones and neurotransmitters, making it a reliable biomarker for neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), such as pheochromocytomas, paragangliomas, and carcinoid tumors.
CGA antibodies are primarily employed in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) to identify and quantify CGA in tissue samples or blood. Their diagnostic utility stems from CGA's high specificity for neuroendocrine differentiation, aiding in distinguishing NETs from non-neuroendocrine malignancies. Additionally, elevated serum CGA levels detected via these antibodies can indicate disease progression or recurrence.
Research also explores CGA's involvement in cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders, broadening the scope of CGA antibody applications. However, factors like renal impairment or proton pump inhibitor use may affect CGA levels, requiring careful interpretation. Despite limitations, CGA antibodies remain indispensable in both clinical diagnostics and experimental studies of neuroendocrine systems.
×