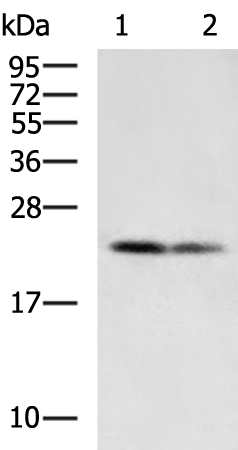
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
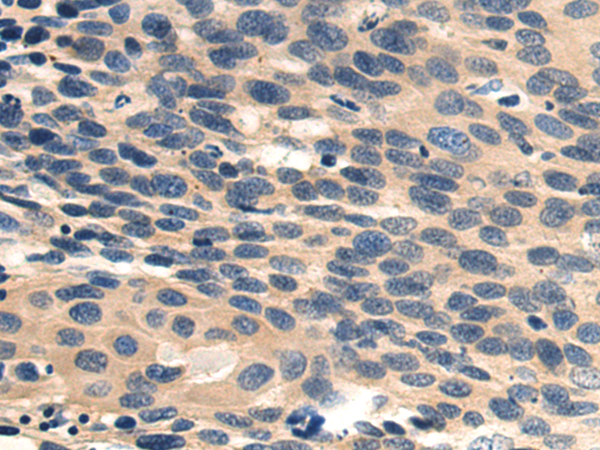
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Dig2; REDD1; REDD-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DDIT4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DDIT4抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(内容为模拟概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"DDIT4 regulates mTOR signaling in hypoxic cancer cells"*
**作者**: Smith A et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用DDIT4抗体通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,验证了DDIT4在低氧条件下对mTORC1通路的抑制作用,发现其在乳腺癌细胞中的高表达与化疗耐药性相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Immunohistochemical analysis of DDIT4 in glioblastoma progression"*
**作者**: Lee J et al.
**摘要**: 通过DDIT4抗体对胶质母细胞瘤组织样本进行免疫组化分析,发现DDIT4表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后不良显著相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"DDIT4 mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis"*
**作者**: Chen R et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用DDIT4抗体在小鼠神经元模型中检测蛋白表达,证实DDIT4通过激活JNK通路介导氧化应激诱导的细胞凋亡,为神经退行性疾病机制提供新见解。
---
**备注**:上述文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“DDIT4 antibody”或“REDD1 antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。
The DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 4 (DDIT4), also known as REDD1 (Regulated in Development and DNA Damage Response 1), is a stress-responsive gene upregulated under hypoxic, DNA-damaging, or nutrient-deprived conditions. It plays a pivotal role in regulating the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway, a central regulator of cell growth, proliferation, and survival. DDIT4 acts as a negative regulator of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) by promoting its inhibition under stress, thereby coordinating cellular energy homeostasis and stress adaptation.
DDIT4 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying DDIT4 protein expression in research settings. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study DDIT4's role in physiological and pathological processes. Dysregulation of DDIT4 has been implicated in cancer, metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes), neurodegenerative diseases, and ischemic injuries, making it a focus for therapeutic targeting.
Antibodies targeting DDIT4 help elucidate its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions with signaling partners like TSC1/TSC2. Validated antibodies with high specificity are critical for distinguishing DDIT4 from homologous proteins (e.g., REDD2) and ensuring reliable experimental outcomes. Research utilizing DDIT4 antibodies continues to advance understanding of stress-response mechanisms, mTOR pathway modulation, and disease progression, highlighting their importance in both basic and translational studies.
×