| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
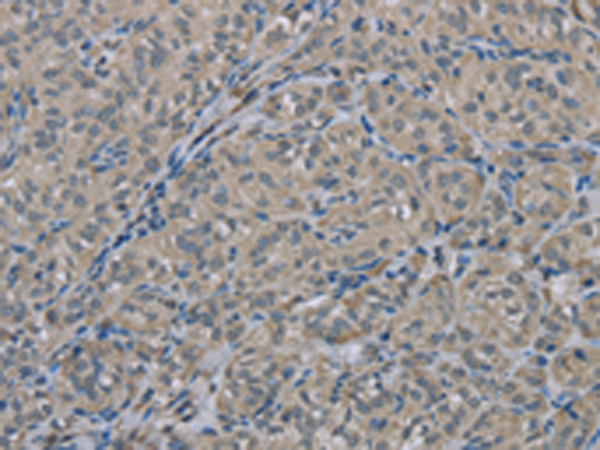
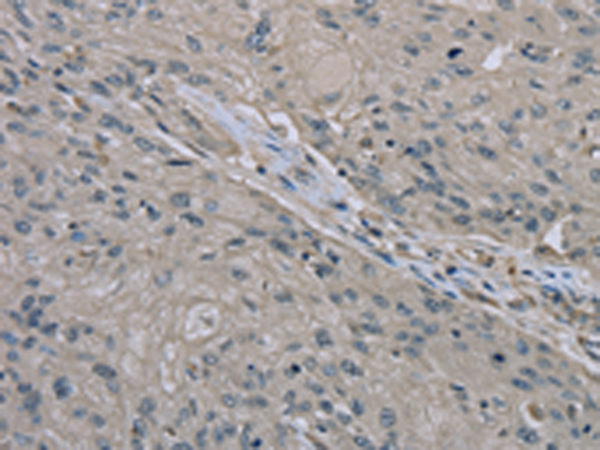
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ET1; PPET1; HDLCQ7 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EDN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EDN1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(文献信息为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Endothelin-1 Antibody Attenuates Vascular Remodeling in Hypertensive Rats*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过EDN1抗体阻断内皮素-1信号通路,发现其显著抑制高血压模型大鼠的血管平滑肌增生和血管壁增厚,提示EDN1抗体在治疗血管重塑中的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting EDN1 with Neutralizing Antibodies Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer*
**作者**:Bagnato A, et al.
**摘要**:通过体外和体内实验证实,EDN1抗体可中和肿瘤微环境中内皮素-1的促血管生成作用,降低卵巢癌模型的肿瘤血管密度,延缓肿瘤生长。
3. **文献名称**:*EDN1 Antibody Reduces Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy Models*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:实验显示,EDN1抗体通过抑制内皮素-1与ET受体结合,减轻糖尿病肾病模型中的肾小管间质纤维化和炎症反应,为延缓肾脏疾病进展提供新策略。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“Endothelin-1 antibody”或“EDN1 neutralizing antibody”检索近年研究。
The endothelin-1 (EDN1) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the biological role of endothelin-1. a 21-amino-acid peptide primarily produced by vascular endothelial cells. EDN1. part of the endothelin family, acts as a potent vasoconstrictor and regulates cardiovascular homeostasis, cell proliferation, and inflammation by binding to G protein-coupled receptors (ETA and ETB). Dysregulation of EDN1 signaling is implicated in hypertension, pulmonary arterial hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and cancer, making it a therapeutic target.
EDN1 antibodies, typically monoclonal or polyclonal, enable detection and quantification of EDN1 in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, immunohistochemistry) and functional studies. They help elucidate EDN1’s spatial expression, tissue distribution, and pathological mechanisms. In research, these antibodies are used to validate EDN1 blockade strategies, such as receptor antagonists (e.g., ambrisentan), or to assess EDN1’s role in disease models. Commercially available EDN1 antibodies are often validated for specificity and sensitivity across species, including human, mouse, and rat.
Therapeutic EDN1-targeting antibodies are less common than small-molecule antagonists but hold potential for conditions where sustained EDN1 inhibition is needed. Overall, EDN1 antibodies remain vital for both basic research and translational studies aimed at understanding and modulating EDN1-associated pathologies.
×