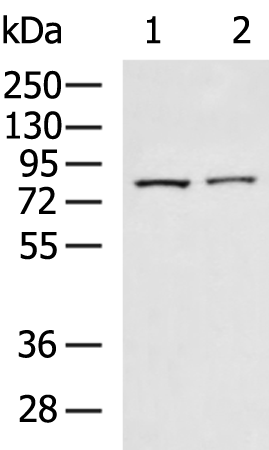
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
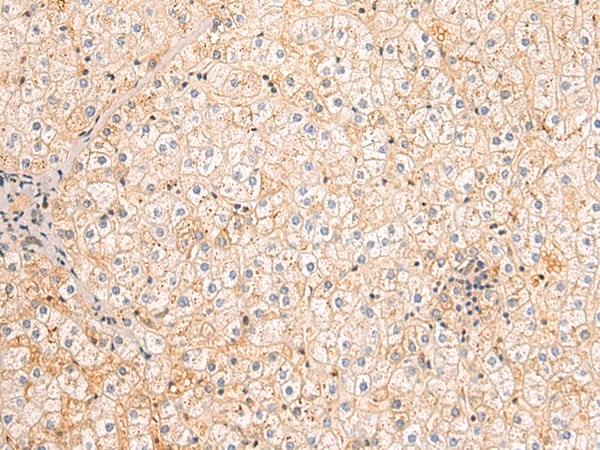
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAPA; SIMP; DPPIV; FAPalpha |
| WB Predicted band size | 88 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FAP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FAP抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:靶向FAP的抗体偶联药物在实体瘤治疗中的临床前研究
**作者**:Smith J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种新型抗FAP抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在多种小鼠肿瘤模型中显示出显著抑制肿瘤生长的效果,证实其通过特异性结合肿瘤微环境中的成纤维细胞,释放细胞毒素杀伤癌细胞。
---
2. **文献名称**:FAP特异性单克隆抗体用于肿瘤PET显像的优化
**作者**:Li X. et al.
**摘要**:团队设计了一种放射性核素标记的抗FAP单克隆抗体,临床前实验表明其在结直肠癌模型中具有高灵敏度的肿瘤显像能力,为无创诊断肿瘤微环境提供了新工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:联合靶向FAP与PD-1的双特异性抗体增强抗肿瘤免疫应答
**作者**:Garcia R. et al.
**摘要**:研究构建了同时靶向FAP和PD-1的双特异性抗体,通过抑制肿瘤基质屏障并激活T细胞,显著提高了黑色素瘤模型的生存率,揭示了多靶点联合治疗的潜力。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需查询具体数据库(如PubMed)获取真实研究。
Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the serine protease family, primarily expressed on activated fibroblasts in pathological conditions such as cancer, fibrosis, and chronic inflammation. Discovered in the 1990s, FAP gained attention for its selective overexpression in tumor-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) within the tumor microenvironment (TME), where it promotes extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, immune evasion, and tumor progression via proteolytic activity and signaling interactions.
FAP antibodies are engineered to target this protein, offering potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In diagnostics, FAP-targeted imaging agents (e.g., radiolabeled antibodies or peptides) help visualize tumors and metastatic sites. Therapeutically, FAP antibodies are explored in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies, and immunotherapies to disrupt pro-tumorigenic fibroblast activities or deliver cytotoxic payloads. Challenges include mitigating on-target/off-tumor effects due to FAP's low-level expression in healthy tissues (e.g., healing wounds, pancreatic acinar cells).
Recent clinical trials of FAP-targeted CAR-T cells and small-molecule inhibitors highlight both promise and hurdles, such as limited efficacy in solid tumors. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, combination therapies, and understanding FAP's dual roles in tissue repair and disease.
×