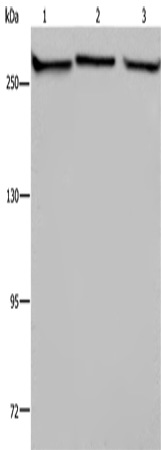
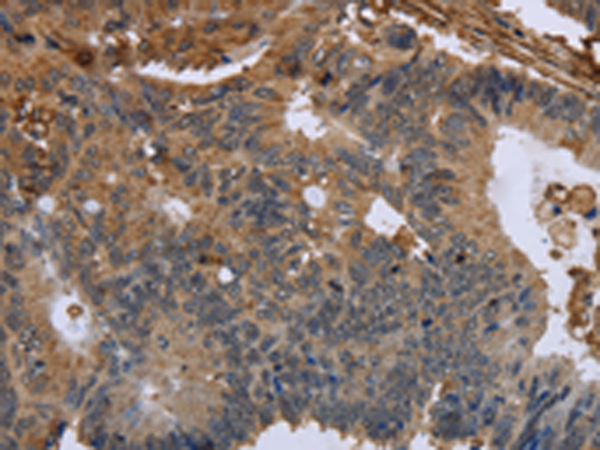
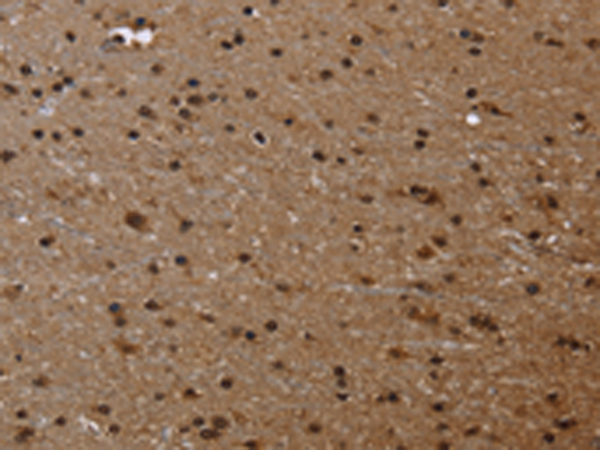
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FLN; FMD; MNS; OPD; ABPX; CSBS; CVD1; FLN1; NHBP; OPD1; OPD2; XLVD; XMVD; FLN-A; ABP-280 |
| WB Predicted band size | 281 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FLNA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于FLNA(Filamin A)抗体的代表性文献,简要整理如下:
1. **文献名称**: *Filamin A: A Multifunctional Scaffolding Protein*
**作者**: Feng Y., Walsh C.A.
**摘要**: 该综述总结了FLNA的结构和功能,强调其作为细胞骨架蛋白在细胞迁移、信号转导中的作用。文中提及FLNA抗体在检测其与整合素、膜受体相互作用中的应用,以及与遗传疾病(如室周结节性异位)的关联。
2. **文献名称**: *X-linked periventricular heterotopia with focal epilepsy caused by mutations in the FLNA gene*
**作者**: Sheen V.L., et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道FLNA基因突变导致X连锁脑室周围结节性异位,通过FLNA抗体免疫组化分析患者脑组织,发现突变导致FLNA蛋白表达缺失,影响神经元迁移和皮层发育。
3. **文献名称**: *Filamin A mediates interactions between cytoskeletal proteins that control cell adhesion and motility*
**作者**: Nakamura F., et al.
**摘要**: 利用FLNA特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示FLNA与β1整合素、Rho GTPases的相互作用机制,阐明其在调节细胞黏附和运动中的关键作用,并建立FLNA缺失细胞的表型分析模型。
4. **文献名称**: *Cloning and characterization of filamin A interacting protein 1 (FILIP1)*
**作者**: Feng Y., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过FLNA抗体筛选人类cDNA文库,发现FILIP1作为FLNA结合蛋白,调控FLNA的降解和细胞骨架重塑,为FLNA在肿瘤转移中的功能提供新证据。
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请核对期刊名称、年份及具体内容。建议通过PubMed或专业数据库查询最新研究。
**Background of FLNA Antibody**
Filamin A (FLNA), encoded by the *FLNA* gene, is a cytoskeletal protein crucial for cell structure, motility, and signaling. It crosslinks actin filaments into dynamic networks, facilitating cell adhesion, migration, and mechanotransduction. FLNA also interacts with integrins, ion channels, and signaling molecules (e.g., β-catenin), influencing pathways like Wnt and NF-κB.
Mutations in *FLNA* are linked to diverse disorders, including X-linked periventricular nodular heterotopia (PVNH, causing neuronal migration defects), frontometaphyseal dysplasia, and cardiovascular abnormalities. FLNA dysfunction may also contribute to cancer metastasis and platelet disorders.
FLNA antibodies are essential tools in research and diagnostics. They detect FLNA expression, localization, and post-translational modifications via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies help study FLNA's roles in cellular processes and disease mechanisms. In clinical contexts, they aid in diagnosing FLNA-related disorders by identifying protein abnormalities in patient tissues. Commercial FLNA antibodies vary in specificity (monoclonal vs. polyclonal) and applications, requiring validation for experimental accuracy. Ongoing research explores FLNA's potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in cancers and genetic syndromes.
×