| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
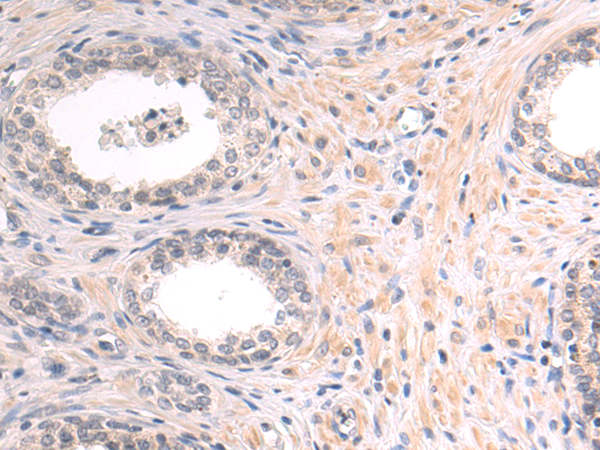
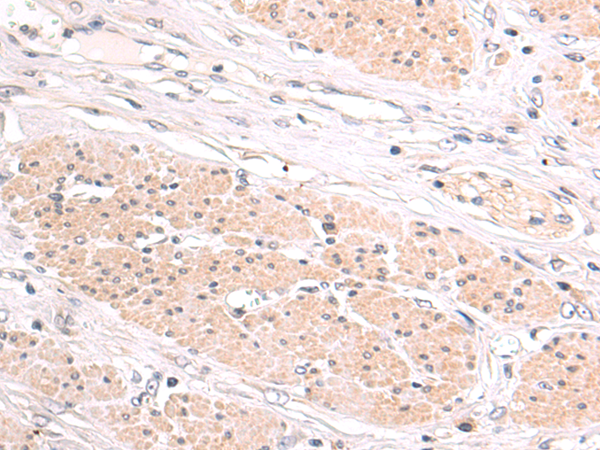
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GPIP4; GCDFP15; GCDFP-15 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human PIP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PIP(抗磷脂酰肌醇抗体)相关的代表性文献,涵盖其临床意义及机制研究:
---
1. **标题**:*Antiphosphatidylinositol antibodies in patients with recurrent spontaneous abortions*
**作者**:Ruffatti A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了抗磷脂酰肌醇抗体(aPI)与复发性流产的关联,发现aPI阳性孕妇的流产风险显著升高,提示其可能通过干扰胎盘血管形成导致妊娠并发症。
---
2. **标题**:*Anti-phospholipid antibodies and β2-glycoprotein-I interaction in thrombosis pathogenesis*
**作者**:de Groot PG, Meijers JCM.
**摘要**:文章综述了抗磷脂抗体(包括抗磷脂酰肌醇抗体)与β2糖蛋白I的相互作用,揭示其在血栓形成中的分子机制,强调抗体通过结合蛋白-磷脂复合物激活内皮细胞和血小板。
---
3. **标题**:*Clinical utility of non-criteria antiphospholipid antibodies in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Tincani A, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了非标准抗磷脂抗体(如抗磷脂酰肌醇、抗磷脂酰丝氨酸)的诊断价值,发现aPI可作为传统抗磷脂抗体检测的补充,尤其在血清阴性抗磷脂综合征患者中具有潜在意义。
---
**备注**:PIP抗体在不同领域可能指向不同靶标(如乳腺癌中的GCDFP-15),上述文献聚焦于自身免疫疾病中的抗磷脂酰肌醇抗体(anti-phosphatidylinositol antibodies)。如需特定方向文献,可进一步补充关键词。
**Background of PIP Antibodies**
PIP (Prolactin-Inducible Protein) antibodies target a small secreted glycoprotein (~15 kDa) encoded by the *PIP* gene, initially identified for its regulation by prolactin in breast tissue. PIP is expressed in various exocrine glands, including mammary, lacrimal, and salivary glands, and plays roles in cell adhesion, immune modulation, and lipid metabolism. Its overexpression in breast cancer, particularly estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) and low-grade tumors, has made it a biomarker of interest in oncology.
PIP antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect PIP expression in tissue samples. In clinical diagnostics, they help distinguish breast carcinoma from other malignancies (e.g., lung or ovarian cancers) due to PIP's tissue-specificity. However, PIP expression is not exclusive to cancer; it also occurs in benign conditions like apocrine metaplasia.
Research suggests PIP may influence tumor progression by modulating immune responses or interacting with CD4+ T cells, though its exact mechanistic role remains unclear. Antibodies against PIP also hold potential as tools for studying protein function or developing targeted therapies. Despite limitations in specificity, PIP antibodies remain valuable in pathology for tumor classification and prognostic evaluation, particularly in breast cancer diagnostics.
×