
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
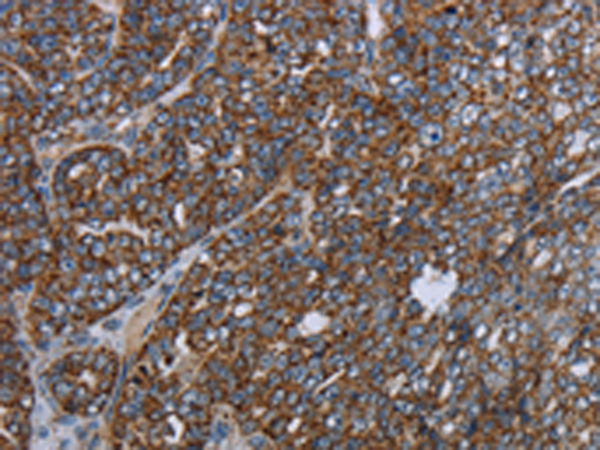
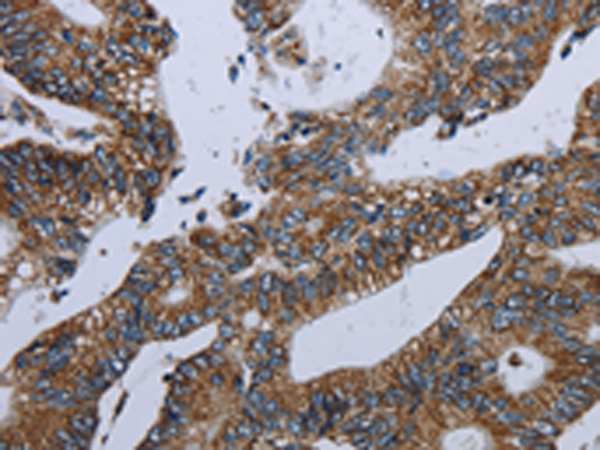
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B16.6; CDA016; CGI-39; GRIM19; GRIM-19 |
| WB Predicted band size | 17 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human NDUFA13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于NDUFA13抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
1. **文献名称**:*GRIM-19/NDUFA13 is a potential biomarker for mitochondrial complex I activity in breast cancer*
**作者**:Huang LS, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用NDUFA13抗体分析乳腺癌细胞中线粒体复合物I亚基GRIM-19(即NDUFA13)的表达,发现其表达水平与复合物I活性降低相关,提示其可能作为乳腺癌代谢异常的潜在标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*NDUFA13 regulates mitochondrial complex I assembly and apoptosis in neuronal cells*
**作者**:Chen Q, et al.
**摘要**:通过NDUFA13抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,研究发现NDUFA13缺失导致线粒体复合物I组装缺陷,并激活神经元细胞凋亡通路,表明其在神经退行性疾病中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based detection of GRIM-19/NDUFA13 in colorectal cancer tissues*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究使用NDUFA13特异性抗体对结直肠癌组织进行免疫组化分析,发现NDUFA13蛋白表达显著下调,且低表达与患者预后不良相关,支持其作为结直肠癌的潜在治疗靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Role of NDUFA13 in virus-induced cell death and innate immunity*
**作者**:Angell JE, et al.
**摘要**:通过NDUFA13抗体验证其在病毒感染模型中的表达变化,研究揭示NDUFA13通过调控线粒体活性影响病毒诱导的细胞死亡和天然免疫应答,为抗病毒机制提供新见解。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需以具体论文内容为准。)
**Background of NDUFA13 Antibody**
NDUFA13 (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A13) is a nuclear-encoded subunit of mitochondrial Complex I, a critical component of the electron transport chain (ETC) responsible for oxidative phosphorylation. As part of the NADH dehydrogenase complex, NDUFA13 contributes to the structural stability and catalytic activity of Complex I, which transfers electrons from NADH to ubiquinone, driving ATP synthesis.
Antibodies targeting NDUFA13 are essential tools for studying mitochondrial function, Complex I assembly, and cellular energy metabolism. These antibodies enable the detection and quantification of NDUFA13 protein levels in tissues or cells via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Dysregulation of NDUFA13 or Complex I deficiency has been linked to mitochondrial disorders (e.g., Leigh syndrome), neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, making such antibodies valuable for both research and clinical diagnostics.
NDUFA13 antibodies are typically raised in host species like rabbits or mice, with validation in specific applications to ensure specificity. Researchers use them to explore mechanisms underlying mitochondrial dysfunction, metabolic reprogramming in cancer, and responses to oxidative stress. Additionally, they aid in identifying biomarkers for diseases associated with impaired energy production. Overall, NDUFA13 antibodies are pivotal in advancing our understanding of mitochondrial biology and its implications in health and disease.
×