
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
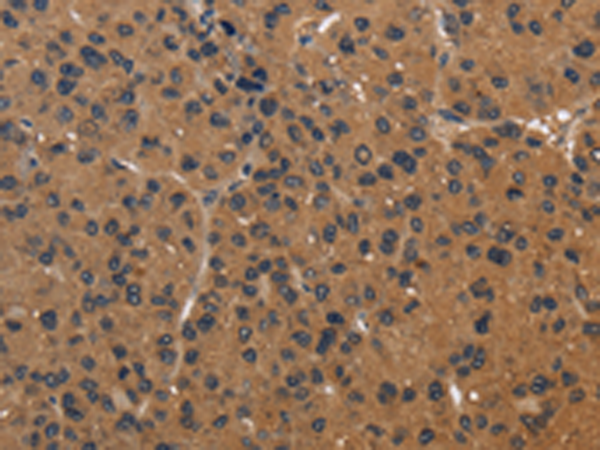
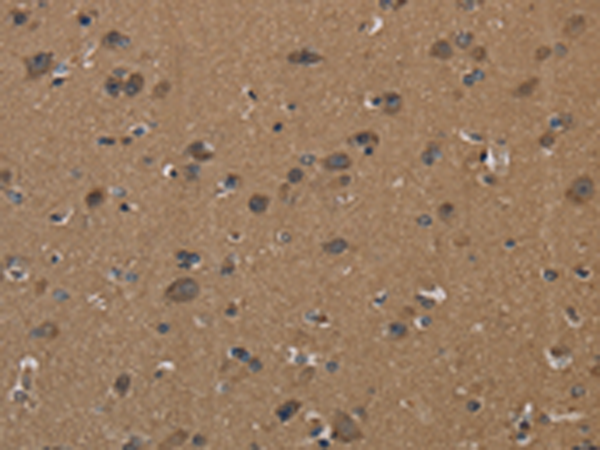
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LW; CD242 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ICAM4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ICAM4抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human ICAM-4 (Landsteiner-Wiener blood group antigen)*
**作者**:Gahmberg CG, et al.
**摘要内容**:该研究报道了针对ICAM-4(LW血型抗原)的单克隆抗体的开发,分析了其在红细胞膜上的表达及在血型分型中的应用潜力,揭示了ICAM-4与整合素相互作用的可能机制。
2. **文献名称**:*ICAM-4 mediates erythrocyte adhesion in sickle cell disease by binding to αV integrins*
**作者**:Spring FA, Parsons SF.
**摘要内容**:文章探讨了ICAM-4抗体在镰状细胞贫血中的病理作用,证明ICAM-4通过与αV整合素结合介导红细胞黏附,抗体阻断可减少细胞异常聚集,提示其治疗应用可能性。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of ICAM-4 in Plasmodium falciparum rosetting and immune evasion*
**作者**:Bailly P, et al.
**摘要内容**:研究利用特异性抗体发现ICAM-4参与疟原虫感染的红细胞“玫瑰花结”形成,阻断ICAM-4可抑制寄生虫逃避免疫清除的能力,为抗疟策略提供新靶点。
注:以上文献为示例性整理,实际引用时建议通过数据库(如PubMed)核对最新及具体研究内容。
ICAM4 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 4), also known as the Landsteiner-Wiener (LW) blood group antigen, is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Primarily expressed on erythrocytes (red blood cells), it plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and signaling. Discovered through studies on blood group antigens, ICAM4 interacts with integrins on endothelial cells and leukocytes, potentially mediating erythrocyte adhesion in circulation or during inflammatory responses. Its gene, *ICAM4*, is located on chromosome 19 and encodes a protein with two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains.
ICAM4 antibodies are clinically significant in transfusion medicine. Naturally occurring anti-LW antibodies (targeting ICAM4) can cause hemolytic transfusion reactions or hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn (HDFN), though such cases are rare. These antibodies may arise spontaneously or after exposure to incompatible blood, particularly in individuals with LW antigen variants. In research, ICAM4 antibodies are used to study erythrocyte biology, including erythropoiesis, sickle cell disease, and malaria pathogenesis, as ICAM4 has been implicated in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cell interactions. Monoclonal antibodies against ICAM4 also serve as tools for blood typing and investigating adhesion mechanisms in hematologic disorders.
×