
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
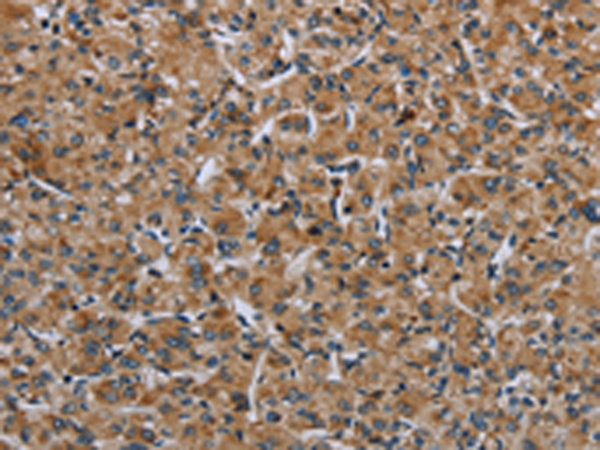
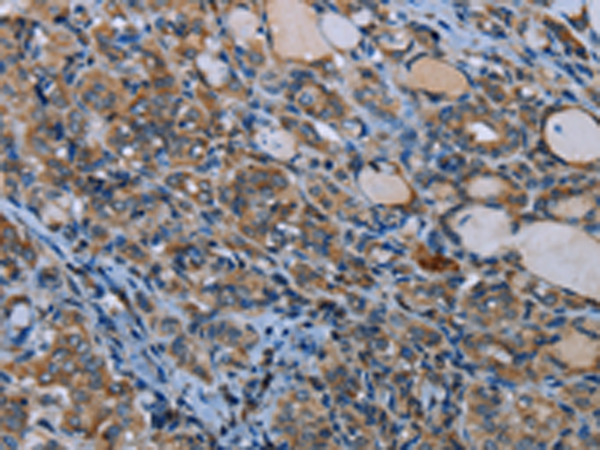
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CRL; GPL; CRL3; GLMR; GLM-R; PLCA2; hGLM-R; IL-31RA; PRO21384 |
| WB Predicted band size | 83 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human IL31RA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与IL-31RA抗体相关的研究文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-IL-31 receptor antibody ameliorates itch and inflammation in murine atopic dermatitis models*
**作者**:Grimstad, Ø., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过小鼠特应性皮炎模型,证明靶向IL-31RA的抗体可显著减少瘙痒行为和皮肤炎症反应,表明IL-31信号通路在介导慢性瘙痒中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Nemolizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized trial*
**作者**:Ruzicka, T., et al.
**摘要**:II期临床试验显示,nemolizumab(抗IL-31RA单抗)可显著改善中重度特应性皮炎患者的瘙痒症状和皮损严重程度,验证了IL-31RA作为治疗靶点的有效性。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of IL-31 and its receptor in pruritus and immune-mediated diseases*
**作者**:Dillon, S.R., et al.
**摘要**:综述了IL-31及其受体IL-31RA在多种瘙痒性疾病(如特应性皮炎、荨麻疹)中的分子机制,并探讨了开发靶向IL-31RA抗体的治疗潜力及临床进展。
---
以上文献聚焦于IL-31RA抗体的机制研究、临床试验及疾病关联,可作为相关领域的核心参考资料。
Interleukin-31 receptor alpha (IL31RA) is a key component of the IL-31 signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in mediating pruritus (itch) and inflammatory responses. As a type I cytokine receptor, IL31RA pairs with the oncostatin M receptor beta (OSMRβ) to form a functional heterodimeric receptor complex. IL-31. the cytokine ligand, is primarily produced by Th2 cells and activates downstream JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/AKT pathways upon binding. This signaling cascade promotes sensory nerve sensitization, skin barrier dysfunction, and immune cell recruitment, making it a central driver in pruritic and inflammatory skin disorders like atopic dermatitis (AD), prurigo nodularis, and allergic contact dermatitis.
IL31RA-targeting antibodies are designed to block IL-31/IL31RA interactions, thereby inhibiting pro-inflammatory and itch-inducing signals. Preclinical studies demonstrate that anti-IL31RA antibodies reduce scratching behavior, epidermal thickening, and immune cell infiltration in disease models. Clinical trials of humanized IL31RA antibodies (e.g., nemolizumab) have shown significant efficacy in alleviating pruritus and lesion severity in AD patients, with some achieving Phase III development. These biologics offer a targeted approach for chronic itch management, addressing an unmet need in dermatology. Ongoing research explores their potential in eosinophilic disorders and neuropathic itch, while combination therapies with other biologics (e.g., dupilumab) are being investigated to enhance therapeutic outcomes.
×