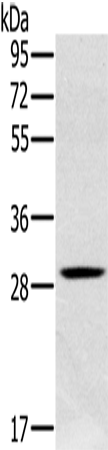
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | G6; NCC27 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CLIC1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLIC1抗体的3篇文献参考,涵盖结构、功能及疾病应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CLIC1 function in cardiac macrophages regulates left ventricular remodeling under pressure overload*
**作者**:Ulmasov B, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过CLIC1特异性抗体进行免疫沉淀和免疫荧光实验,发现CLIC1在心脏巨噬细胞中调控炎症反应,并影响压力超负荷下的左心室重构。抗体被用于验证CLIC1的蛋白表达及亚细胞定位。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of the CLIC1 transmembrane domain and its antibody interaction sites*
**作者**:Valenzuela SM, et al.
**摘要**:作者解析了CLIC1的跨膜结构域,并利用单克隆抗体进行表位定位,揭示了抗体结合对CLIC1通道功能的抑制作用,为靶向CLIC1的抗体药物开发提供结构基础。
3. **文献名称**:*CLIC1 antibody targeting suppresses glioblastoma growth by disrupting intracellular chloride homeostasis*
**作者**:Setti M, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种抗CLIC1的中和性抗体,通过阻断其离子通道功能,破坏胶质母细胞瘤细胞的氯离子稳态,显著抑制肿瘤生长。抗体在体内外实验中均表现出治疗潜力。
---
以上文献均涉及CLIC1抗体的开发或应用,涵盖基础机制研究与临床前治疗探索。如需具体发表年份或期刊,可进一步补充检索。
**Background of CLIC1 Antibody**
The **Chloride Intracellular Channel 1 (CLIC1)** protein belongs to the CLIC family of chloride ion channels, which exhibit unique dual functionality as both soluble cytoplasmic proteins and integral membrane proteins. CLIC1 is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including ion homeostasis, cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and cellular proliferation. Its redox-sensitive structure allows it to transition between soluble and membrane-bound states, influencing ion transport and intracellular signaling pathways.
CLIC1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying the expression, localization, and functional roles of CLIC1 in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry. Research has highlighted CLIC1's overexpression in various cancers (e.g., glioblastoma, colorectal, and breast cancers), where it correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis. This has spurred interest in CLIC1 as a potential therapeutic target or biomarker.
Additionally, CLIC1 antibodies aid in exploring its involvement in inflammatory diseases, neurological disorders, and oxidative stress responses. Studies also investigate its interaction with cytoskeletal components and signaling molecules, shedding light on its non-channel roles in cellular dynamics. As CLIC1's mechanistic complexity remains under active investigation, high-specificity antibodies remain critical for advancing its biological and clinical understanding.
×