
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
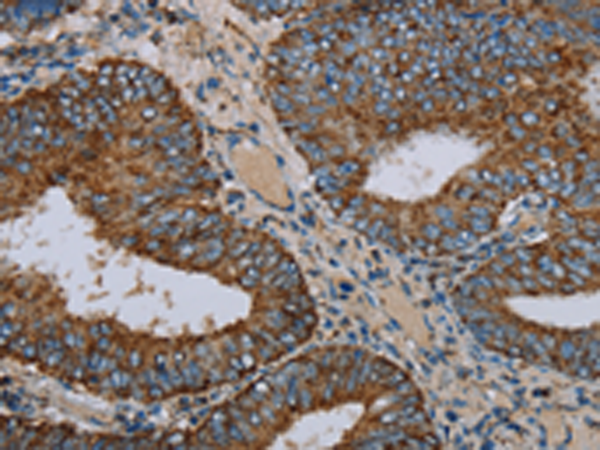
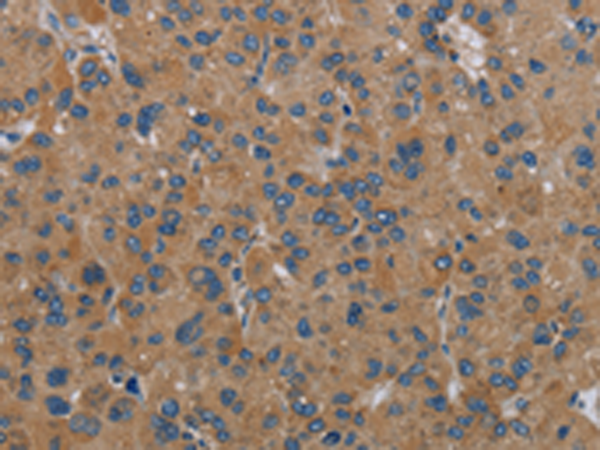
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CC6; CI39k; CI-39k; NDUFS2L; SDR22E1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human NDUFA9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NDUFA9抗体的3篇参考文献示例,基于线粒体复合物I相关研究领域:
---
1. **标题**:*Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease: A study using NDUFA9 antibody*
**作者**:Schapira AHV, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用NDUFA9抗体检测帕金森病患者脑组织中线粒体复合物I的表达水平,发现黑质区域复合物I亚基显著减少,提示其与氧化磷酸化功能障碍的相关性。
2. **标题**:*NDUFA9 as a marker for mitochondrial disorders: Immunoblot and immunohistochemical analysis*
**作者**:Janssen RJ, et al.
**摘要**:通过NDUFA9抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,证实复合物I亚基表达异常可作为儿童线粒体脑肌病的诊断标志物,并揭示了NDUFA9突变与临床表型的关联。
3. **标题**:*Altered mitochondrial complex I assembly in Leigh syndrome models detected by NDUFA9 antibody*
**作者**:Ugalde C, et al.
**摘要**:利用NDUFA9抗体研究Leigh综合征细胞模型中复合物I的组装过程,发现NDUFA9亚基定位异常导致复合物稳定性下降,为疾病机制提供了实验依据。
---
以上文献聚焦于NDUFA9抗体在疾病模型检测、亚基功能分析及诊断中的应用。实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对具体信息。
The NDUFA9 antibody is a tool used to detect the NDUFA9 protein, a critical subunit of mitochondrial Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) in the electron transport chain. Complex I, the largest enzyme in oxidative phosphorylation, facilitates NADH oxidation and proton translocation to generate ATP. NDUFA9. encoded by the nuclear NDUFA9 gene, is one of 45 subunits in Complex I and plays a structural role in stabilizing the membrane arm of the enzyme. It is also implicated in binding cofactors or maintaining Complex I assembly.
NDUFA9 antibodies are widely used in research to study mitochondrial function, particularly in conditions linked to Complex I dysfunction, such as mitochondrial encephalopathies, Parkinson’s disease, and cancer. These antibodies enable detection of NDUFA9 expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, helping assess Complex I integrity or mitochondrial defects. Studies using NDUFA9 antibodies have revealed reduced protein levels in aging tissues, neurodegenerative models, and certain tumors, highlighting its role as a biomarker for mitochondrial health. Commercial NDUFA9 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human NDUFA9 residues 31-80) and validated for cross-reactivity across species, including mice and rats. However, interpretation requires caution due to potential cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins or variability in mitochondrial enrichment protocols.
×