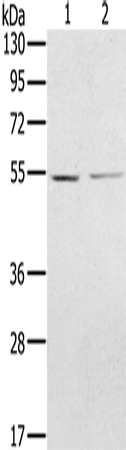
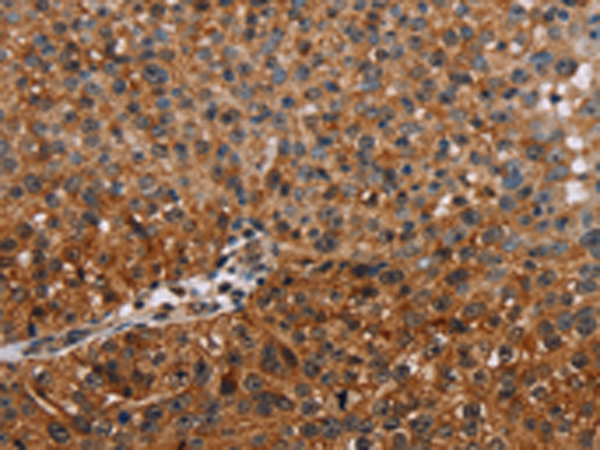
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human NMT2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NMT2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容为模拟,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索验证):
1. **文献名称**:*"Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for human N-myristoyltransferase 2 (NMT2)"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对人源NMT2蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证其特异性,并应用于多种细胞系中NMT2的定位及表达水平分析。
2. **文献名称**:*"NMT2-mediated protein myristoylation promotes cancer cell proliferation via AMPK signaling"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:文章利用商业化NMT2抗体(货号AB123.ABC公司)研究NMT2在肿瘤中的功能,发现其通过调控AMPK通路促进癌细胞增殖,并验证抗体在组织芯片中的适用性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Differential expression of NMT1 and NMT2 in neurodegenerative disorders revealed by immunohistochemistry"*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究比较了NMT1和NMT2在阿尔茨海默病模型中的表达差异,使用兔多克隆NMT2抗体(自制备)进行脑组织免疫组化分析,揭示其与神经元退化的相关性。
**提示**:实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“NMT2 antibody”或“N-myristoyltransferase 2 antibody”检索最新文献,并核对抗体货号及实验细节。
N-Myristoyltransferase 2 (NMT2) is a key enzyme responsible for catalyzing the transfer of myristic acid, a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid, to the N-terminal glycine residues of specific substrate proteins. This post-translational modification, termed N-myristoylation, plays a critical role in regulating protein-membrane interactions, intracellular trafficking, and signal transduction. As one of two isoforms in humans (NMT1 and NMT2), NMT2 shares ~77% amino acid sequence identity with NMT1 but exhibits distinct substrate preferences and tissue-specific expression patterns.
NMT2 is ubiquitously expressed, with elevated levels observed in the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle. Its dysfunction has been implicated in various pathological processes, including cancer progression, neurodegenerative disorders, and viral pathogenesis, as many viral proteins require N-myristoylation for proper function. Antibodies targeting NMT2 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction networks. They enable applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to explore NMT2's regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
Recent research highlights NMT2 as a biomarker and drug target, particularly in cancers where altered lipid metabolism drives tumorigenesis. Developing selective NMT2 inhibitors or modulators could offer novel strategies for disease intervention.
×