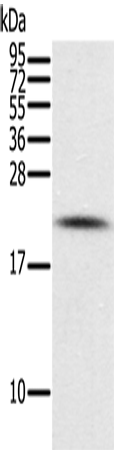
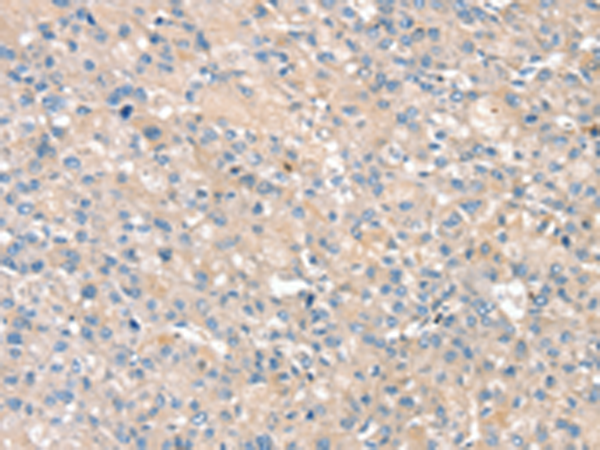
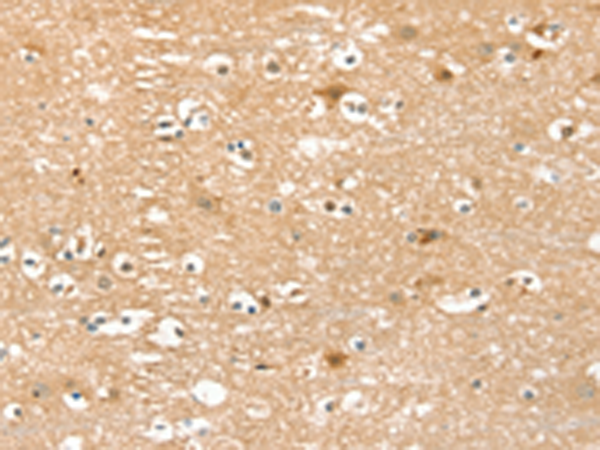
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DOD; UBL5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human PIN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于PIN1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"Prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a molecular target for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics"*
**作者**:Lu, K.P., Zhou, X.Z.
**摘要**:该研究探讨Pin1在癌症中的关键作用,指出其通过异构化磷酸化蛋白调控细胞周期和信号通路。研究利用Pin1抗体验证其在多种癌细胞中过表达,并强调其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*"Role of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 in Alzheimer’s disease"*
**作者**:Wulf, G., et al.
**摘要**:文章揭示Pin1与阿尔茨海默病的关联,发现Pin1抗体可检测磷酸化tau蛋白的构象变化,表明Pin1缺失导致tau异常聚集,提示其作为神经退行性疾病生物标志物的可能性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Pin1 overexpression enhances β-catenin activation and promotes tumorigenesis"*
**作者**:Yeh, E.S., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用Pin1抗体)和功能实验,研究发现Pin1通过稳定β-catenin促进肿瘤发生,为靶向Pin1-Wnt通路提供理论依据。
4. **文献名称**:*"Structural and functional analysis of Pin1 antibodies for selective inhibition in oncogenesis"*
**作者**:Nakamura, K., et al.
**摘要**:研究开发高特异性Pin1抗体,解析其结合表位,并证明其选择性抑制Pin1的酶活性,为开发抗癌药物提供新策略。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed等数据库核对原文。)
PIN1 (Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1) is a unique enzyme belonging to the parvulin family of prolyl isomerases. It specifically catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of phosphorylated serine/threonine-proline (pSer/Thr-Pro) motifs in target proteins, modulating their conformation, stability, and activity. PIN1 plays critical roles in regulating cell cycle progression, gene transcription, DNA damage response, and apoptosis. Its dysregulation is implicated in various diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and immune disorders. In cancer, PIN1 is often overexpressed and promotes oncogenic signaling by stabilizing activated kinases (e.g., β-catenin, cyclin D1) or inactivating tumor suppressors (e.g., p53). Conversely, in Alzheimer’s, PIN1 dysfunction correlates with hyperphosphorylated tau aggregation and neurodegeneration.
PIN1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting PIN1 expression and studying its biological functions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess PIN1 levels, subcellular localization, and interactions in tissues or cultured cells. Specific monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies help researchers explore PIN1's role in disease mechanisms, therapeutic targeting, and biomarker discovery. Validated PIN1 antibodies are critical for ensuring specificity in experimental models, particularly given PIN1's structural complexity and post-translational modifications. Ongoing research continues to highlight PIN1 as a promising therapeutic target, driving demand for reliable antibodies in both basic and translational studies.
×