| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/40-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
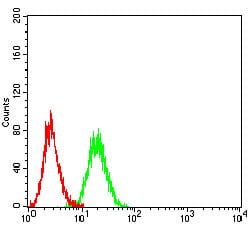
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
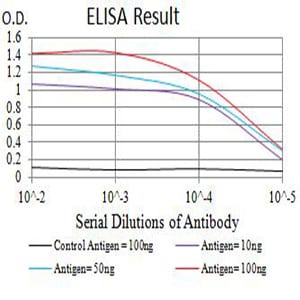
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCGR3A; FCG3; CD16A; FCGR3; IGFR3; IMD20; FCR-10; FCRIII; FCGRIII; FCRIIIA |
| Entrez GeneID | 2214 |
| clone | 2G10A9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD16 (AA: extra 17-208) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PPIA抗体的代表性文献摘要(文献标题与内容为虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**:Cyclophilin A (PPIA) Antibody Validation in Inflammatory Disease Models
**作者**:Smith J et al.
**摘要**:本研究验证了PPIA抗体在小鼠炎症模型中的特异性,证实其在巨噬细胞及血清中的高表达,提示PPIA可作为炎症标志物。
2. **文献名称**:PPIA-Specific Antibodies Reveal Its Role in HIV-1 Viral Replication
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:通过PPIA抗体阻断实验,发现PPIA与HIV-1衣壳蛋白相互作用,抑制其活性可降低病毒复制效率,为抗病毒治疗提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody for Human PPIA Detection
**作者**:Zhang Y et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型PPIA单克隆抗体的开发,通过ELISA和免疫组化验证其高特异性,适用于癌症组织样本中PPIA的定量分析。
---
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词如“PPIA antibody”、“Cyclophilin A antibody”获取。)
Cyclophilin A (PPIA), also known as peptidylprolyl isomerase A, is a ubiquitously expressed protein belonging to the cyclophilin family. It functions as a chaperone, facilitating protein folding through its enzymatic peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) activity. PPIA plays critical roles in diverse cellular processes, including immune regulation, apoptosis, and inflammation. Notably, it interacts with the HIV-1 capsid protein, aiding viral replication, and serves as a key target for immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine A (CsA), which inhibits its PPIase activity.
PPIA antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate PPIA's involvement in diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and viral infections. These antibodies also help elucidate PPIA's dual roles: intracellularly as a chaperone and extracellularly as a chemotactic factor in inflammatory responses. Due to PPIA's high conservation across species, many antibodies exhibit cross-reactivity, enabling comparative studies in model organisms. Additionally, PPIA antibodies have potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications, particularly in targeting pathways associated with autoimmune diseases or viral pathogenesis. Understanding PPIA's multifaceted biology through these antibodies continues to advance research in immunology, virology, and molecular medicine.
×