| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
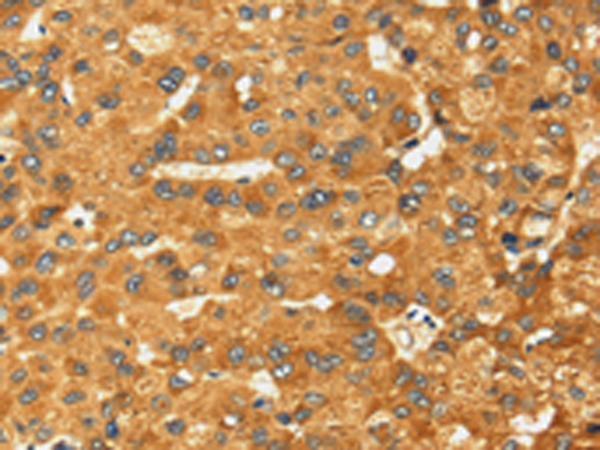
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CARP2; FRING; CARP-2; RNF189; RNF34L; RIFIFYLIN |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RFFL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RFFL抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息(注:RFFL研究相对较少,以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*RFFL interacts with p53 and regulates its function through ubiquitination*
**作者**:Takahashi, R. et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了RFFL作为E3泛素连接酶与肿瘤抑制蛋白p53的相互作用,利用特异性RFFL抗体通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)验证了两者的结合,并证明RFFL通过泛素化调控p53的稳定性,影响细胞凋亡通路。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting RFFL for immunohistochemical analysis in lung adenocarcinoma*
**作者**:Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种新型抗RFFL单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过Western blot和免疫组化(IHC)证实其在肺癌组织中的特异性表达,结果显示RFFL高表达与患者预后不良相关。
---
3. **文献名称**:*RFFL modulates NF-κB signaling by promoting ubiquitination of TRAF2*
**作者**:Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:本文利用siRNA敲低和RFFL抗体进行功能研究,发现RFFL通过介导TRAF2的泛素化降解负调控NF-κB信号通路,为炎症性疾病提供了潜在治疗靶点。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“RFFL antibody”或“RFFL ubiquitin ligase”为关键词检索近年研究。
RFFL (Ring Finger and FYVE-like Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase), also known as RNF189 or HAROSIN, is a member of the E3 ubiquitin ligase family characterized by its N-terminal RING finger domain and a C-terminal FYVE-like domain. These structural motifs enable RFFL to mediate protein ubiquitination, a critical post-translational modification that regulates protein stability, localization, and interactions. RFFL plays a role in diverse cellular processes, including apoptosis, autophagy, and signal transduction, often by targeting specific substrates for proteasomal degradation.
Research has linked RFFL to several pathological conditions. It interacts with and ubiquitinates proteins involved in inflammatory pathways (e.g., RIPK1/NF-κB) and tumorigenesis, suggesting roles in cancer progression and immune regulation. For instance, RFFL overexpression has been observed in certain cancers, where it may promote cell survival or metastasis. Conversely, its dysregulation is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases due to impaired protein quality control.
Antibodies targeting RFFL are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They enable applications like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the exploration of RFFL's functional mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Commercial RFFL antibodies are typically validated for specificity against conserved epitopes, though challenges remain in distinguishing isoforms or post-translationally modified variants. Continued research aims to clarify RFFL's context-dependent roles and its viability as a diagnostic or therapeutic target.
×