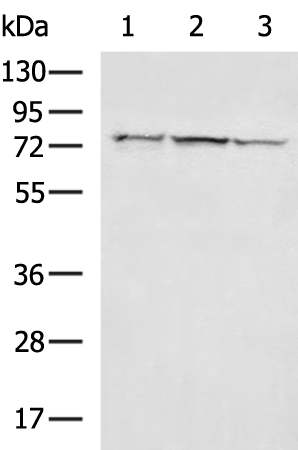
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
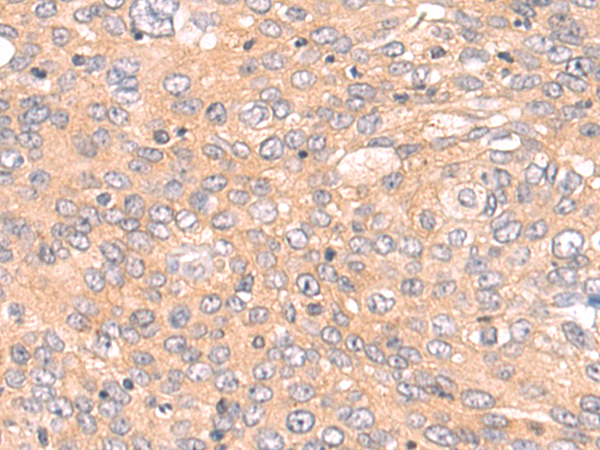
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RIP; RIP1; AIEFL; IMD57; RIP-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 76 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RIPK1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RIPK1抗体的代表性文献摘要信息(基于公开研究整理,具体文献请核实原始来源):
---
1. **文献名称**: *RIPK1 ensures apoptosis through dual regulation of the caspase-8/FADD/cFLIP axis*
**作者**: Newton, K. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用特异性RIPK1抗体揭示其在细胞凋亡中的双重调控机制,通过抑制caspase-8活性或促进FADD/cFLIP复合体形成,决定细胞存活或死亡路径。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation*
**作者**: He, S. et al.
**摘要**: 通过RIPK1抗体免疫共沉淀技术,验证了RIPK1与RIP3的磷酸化依赖复合物形成机制,阐明其在病毒触发坏死性凋亡(necroptosis)和炎症反应中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *RIPK1 mediates axonal degeneration by promoting inflammation and necroptosis in ALS*
**作者**: Ito, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用RIPK1特异性抗体在肌萎缩侧索硬化(ALS)模型中证明,抑制RIPK1活性可减少神经元轴突变性,提示其通过激活炎症和坏死性凋亡通路驱动疾病进展。
---
**备注**:建议通过PubMed或Web of Science平台,以“RIPK1 antibody”及“kinase activity/necroptosis/inflammation”为关键词检索最新文献,优先选择高被引论文或权威期刊(如*Nature*, *Cell*)的研究。
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) is a key regulator of cell survival, apoptosis, and necroptosis, playing a dual role in signaling pathways downstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and other death receptors. Structurally, RIPK1 contains an N-terminal kinase domain, an intermediate domain, and a C-terminal death domain that facilitates interactions with other signaling molecules. Under normal conditions, RIPK1 promotes NF-κB activation and pro-survival signaling, but upon caspase-8 inhibition or specific post-translational modifications (e.g., ubiquitination or phosphorylation), it can form the necrosome complex with RIPK3 and MLKL to execute necroptosis.
RIPK1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activation status in various biological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry to investigate RIPK1's role in inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., ALS, Alzheimer's), and cancer. Specific antibodies targeting phosphorylated forms (e.g., Ser166) help identify activated RIPK1 in necroptosis pathways. Validation often involves knockout cell lines or RIPK1 kinase inhibitors (e.g., Necrostatin-1) to confirm specificity.
Dysregulation of RIPK1 is linked to pathological conditions, making its antibodies critical for both mechanistic research and therapeutic development. Recent studies also explore RIPK1's non-canonical roles in autophagy and innate immunity, expanding the utility of these reagents in interdisciplinary research.
×