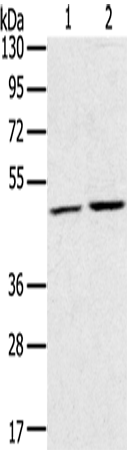
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GTR2; RAGC; TIB929 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RRAGC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及RRAGC抗体的参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:Rag GTPases mediate amino acid-dependent recruitment of TFEB and MITF to lysosomes
**作者**:Martina, J. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用RRAGC抗体验证基因敲除细胞中蛋白缺失,揭示RRAGC与TFEB转录因子在溶酶体生物合成中的调控关系,证实氨基酸信号通过Rag GTPase-mTORC1通路调控细胞代谢。
2. **文献名称**:Spatial control of the TSC complex integrates insulin and nutrient regulation of mTORC1 at the lysosome
**作者**:Menon, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过RRAGC抗体进行免疫荧光和免疫共沉淀实验,证明RRAGC与Ragulator复合体协同调控mTORC1在溶酶体的定位,揭示胰岛素和氨基酸信号整合机制。
3. **文献名称**:Regulation of mTORC1 by the Rag GTPases is necessary for neonatal autophagy and survival
**作者**:Efeyan, A. et al.
**摘要**:利用RRAGC特异性抗体检测小鼠模型中蛋白表达水平,发现RRAGC缺失导致mTORC1信号异常及自噬缺陷,强调其在新生儿代谢适应中的必要性。
注:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用需核对具体论文。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以"RRAGC antibody"+"mTORC1"等关键词搜索最新研究。
The RRAGC antibody is a research tool used to detect and study the RRAGC protein (Ras-related GTP-binding protein C), a key component of the Rag GTPase family involved in nutrient-sensing signaling pathways. RRAGC forms heterodimers with RRAGA or RRAGB, functioning as critical regulators of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). This complex coordinates cellular growth and metabolism by sensing amino acid availability. Upon amino acid sufficiency, Rag GTPases recruit mTORC1 to lysosomal surfaces, activating its kinase activity to promote anabolic processes like protein synthesis and inhibit autophagy.
RRAGC antibodies are widely utilized in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate RRAGC expression, localization, and interactions in diverse biological contexts. Dysregulation of RRAGC and mTORC1 signaling is implicated in cancers, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, making these antibodies valuable for studying disease mechanisms. Mutations or altered expression of RRAGC have been linked to tumorigenesis and metabolic reprogramming, underscoring its role as a potential therapeutic target. Researchers also employ RRAGC antibodies to explore nutrient-responsive pathways, lysosomal function, and cellular stress responses, contributing to advancements in precision medicine and drug development targeting mTOR-related pathologies.
×