| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
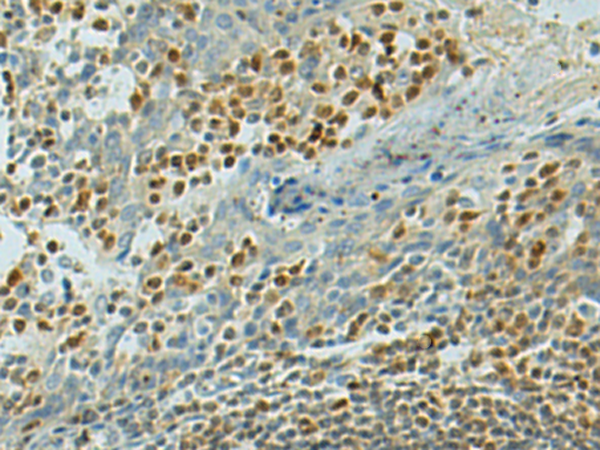
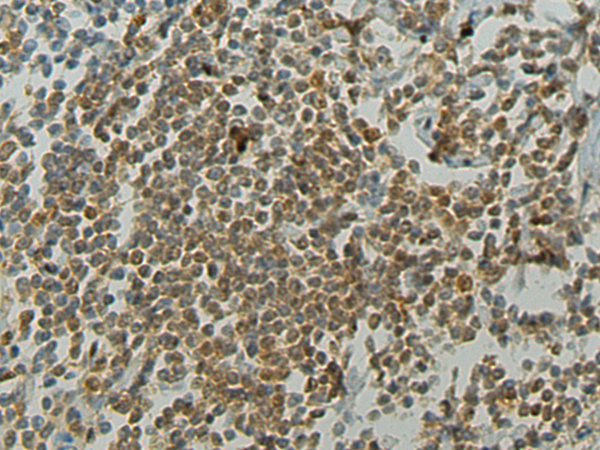
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TCFEB; BHLHE35; ALPHATFEB |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TFEB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TFEB抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
1. **"A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy"**
- **作者**: Settembre C, Di Malta C, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示了TFEB通过调控溶酶体和自噬相关基因的表达,响应细胞营养状态的变化。研究使用TFEB抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot,证实饥饿状态下TFEB核转位增加,促进溶酶体生成(*Science*, 2011)。
2. **"The nutrient-responsive transcription factor TFEB coordinates autophagy and lysosome biogenesis"**
- **作者**: Martina JA, Puertollano R.
- **摘要**: 本文阐明了mTORC1通过磷酸化调控TFEB的亚细胞定位。利用TFEB抗体的免疫沉淀和免疫荧光实验,证明mTORC1抑制时TFEB入核激活自噬通路(*Nature Communications*, 2014)。
3. **"TFEB–MITF signalling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma"**
- **作者**: Slade L, Biswas D, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现肾透明细胞癌中TFEB表达异常,并与患者预后相关。通过TFEB抗体的免疫组化分析,显示其核定位与肿瘤侵袭性相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物(*Oncogene*, 2017)。
4. **"TFEB-mediated autophagy rescues midbrain dopamine neurons from α-synuclein toxicity"**
- **作者**: Decressac M, Mattsson B, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究证明TFEB过表达通过增强自噬清除α-突触核蛋白,保护帕金森病模型中的多巴胺神经元。使用TFEB抗体验证了其在中脑神经元中的表达上调(*Brain*, 2013)。
这些文献均利用TFEB抗体在分子机制或疾病模型中探究其功能,涵盖定位、表达调控及治疗潜力。
Transcription factor EB (TFEB) is a member of the MiT/TFE family of basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors, known for regulating lysosomal biogenesis, autophagy, and cellular stress responses. It coordinates the expression of genes involved in lysosomal function, nutrient sensing, and energy metabolism by binding to CLEAR (Coordinated Lysosomal Expression and Regulation) elements in their promoters. TFEB activity is tightly controlled by its subcellular localization: under nutrient-rich conditions, TFEB is phosphorylated by mTORC1 and retained in the cytoplasm, while starvation or lysosomal stress triggers its dephosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and activation of target genes.
Antibodies against TFEB are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and regulatory mechanisms. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess TFEB levels in cell lines, tissues, or disease models. Such antibodies help researchers investigate TFEB's role in pathological conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease), and lysosomal storage diseases. Specific TFEB antibodies can also distinguish post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation states) or mutations affecting its function. Given TFEB's emerging role as a therapeutic target for diseases involving lysosomal dysfunction or metabolic imbalances, reliable antibodies are essential for both basic research and preclinical studies aiming to modulate TFEB activity for therapeutic benefit.
×