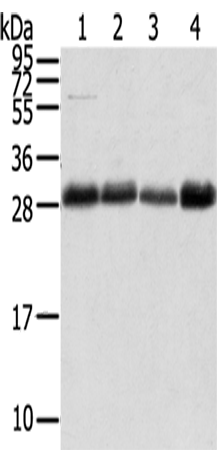
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
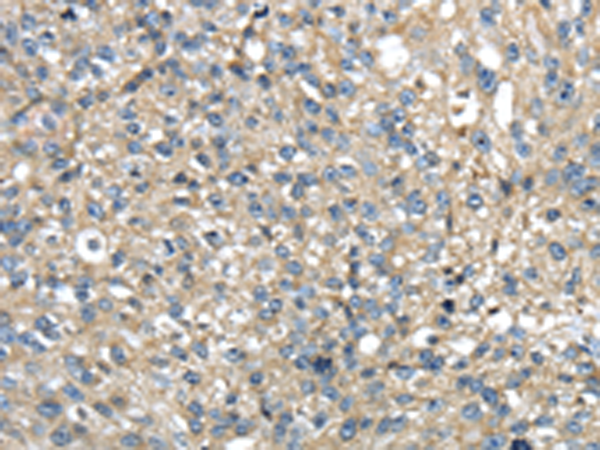
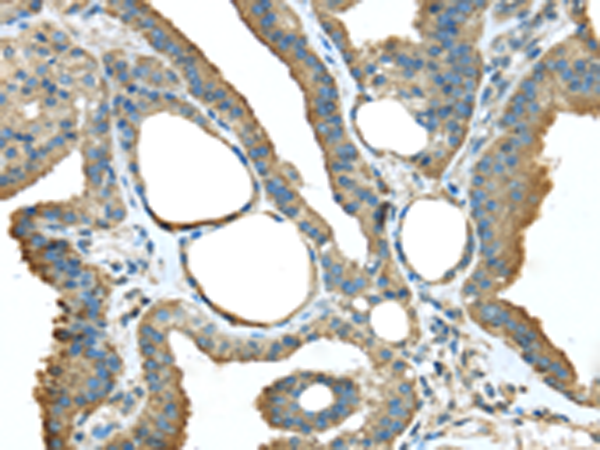
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tp24; Il1rl1l; IL1RL1LG |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TMED1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TMED1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分信息为示例性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**:*"TMED1 modulates protein secretion and cellular stress responses"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用TMED1抗体通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示了TMED1在内质网-高尔基体蛋白转运中的作用,并发现其缺失会加剧细胞在氧化应激下的凋亡。
2. **文献名称**:*"TMED1 regulates cancer cell proliferation via EGFR signaling"*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:通过TMED1抗体进行免疫组化分析,作者发现TMED1在结直肠癌组织中高表达,并通过调控EGFR信号通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*"TMED1 mediates ER-Golgi transport of GPI-anchored proteins"*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究使用TMED1抗体进行免疫共沉淀和共聚焦显微镜观察,证明TMED1特异性参与GPI锚定蛋白的运输,并维持细胞膜蛋白稳态。
4. **文献名称**:*"TMED1 antibody characterization in neurodegenerative models"*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:通过TMED1抗体检测阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织,发现TMED1表达水平与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积呈负相关,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的潜在作用。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“TMED1 antibody”或“TMED1 + [研究领域]”获取真实文献。
TMED1 (Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 1), also known as p24a or EMP24. is a member of the TMED family involved in intracellular protein trafficking and cargo receptor activities. It plays a role in the formation of COPII vesicles, which mediate endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi transport, and is implicated in the selective packaging of secretory proteins. TMED1 is widely expressed in epithelial, immune, and neuronal cells, influencing processes like inflammation, cell differentiation, and signaling pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin.
TMED1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies, typically monoclonal or polyclonal (derived from rabbits or mice), are used in techniques including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. They help detect endogenous TMED1 in tissues or cultured cells, aiding research into its physiological and pathological roles.
Dysregulation of TMED1 has been linked to diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic conditions. In cancer, elevated TMED1 levels correlate with tumor progression, potentially affecting cell migration and angiogenesis. In Alzheimer’s disease, TMED1 may interact with amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking. Antibodies against TMED1 thus serve as critical reagents for exploring its diagnostic or therapeutic potential. Recent studies also highlight its role in viral infections (e.g., SARS-CoV-2) by modulating host cell entry pathways, underscoring its broad biomedical relevance.
×