| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
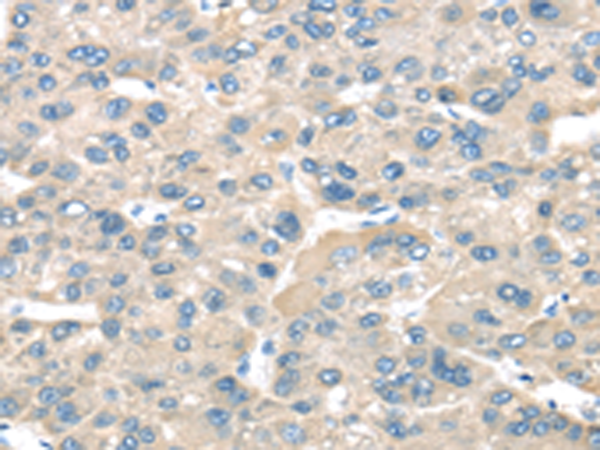
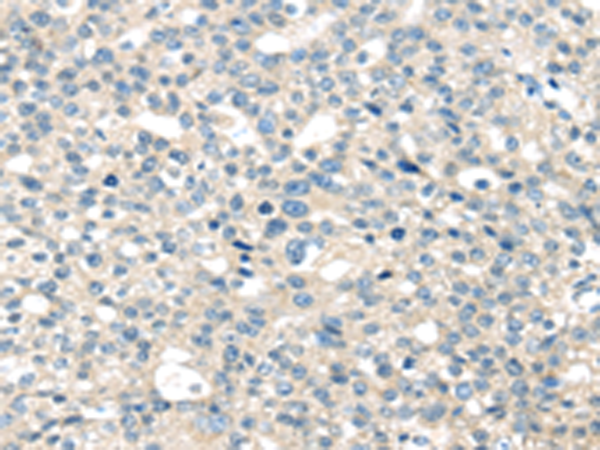
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NDED; GG2-1; SCCS2; SCC-S2; MDC-3.13 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"TNFα-induced protein 8-like 2 (TIPE2) as a novel regulator of tumor immunity"**
- **作者**: Lou Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用抗TNFAIP8(TIPE2)抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,分析其在多种肿瘤组织中的表达,发现其通过调控炎症因子信号通路抑制肿瘤生长,提示其作为免疫治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for TNFAIP8 in human cancers"**
- **作者**: Kumar D, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗人TNFAIP8单克隆抗体,验证了其在结直肠癌和肺癌组织中的敏感性及特异性,并证明TNFAIP8高表达与患者预后不良相关。
3. **"TNFAIP8 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in glioblastoma through AKT signaling"**
- **作者**: Wang Z, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过抗TNFAIP8抗体进行功能研究,发现其通过激活AKT通路促进胶质母细胞瘤的增殖和侵袭,为靶向TNFAIP8的抑制剂开发提供理论依据。
4. **"TNFAIP8 regulates apoptosis and autophagy in macrophages during sepsis"**
- **作者**: Li Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 使用抗TNFAIP8抗体研究其在脓毒症模型中的作用,发现其通过抑制自噬和促进凋亡加剧炎症反应,揭示了其在败血症病理中的关键调控机制。
TNFAIP8 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Induced Protein 8) is a family of proteins involved in regulating cell survival, apoptosis, and immune responses. It plays dual roles in cancer and inflammation, acting either as an oncogene or tumor suppressor depending on cellular context. TNFAIP8 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance in various cancers by modulating signaling pathways like PI3K/AKT and NF-κB. In immunity, it regulates T-cell activation and inflammatory responses, linking it to autoimmune diseases and infections.
TNFAIP8 antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies (monoclonal or polyclonal) are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to quantify TNFAIP8 levels in tissues or cell lines. Researchers employ them to explore TNFAIP8’s role in tumor progression, immune evasion, and therapy resistance. Commercially available antibodies often target conserved regions, with validation across species like human, mouse, and rat.
Recent studies highlight TNFAIP8 as a potential biomarker for cancer prognosis and a therapeutic target. Antibodies against TNFAIP8 also aid in developing diagnostic assays and evaluating experimental inhibitors. However, specificity and cross-reactivity challenges require careful validation. Understanding TNFAIP8’s mechanisms through antibody-based research remains pivotal for advancing cancer immunology and targeted therapies.
×