| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
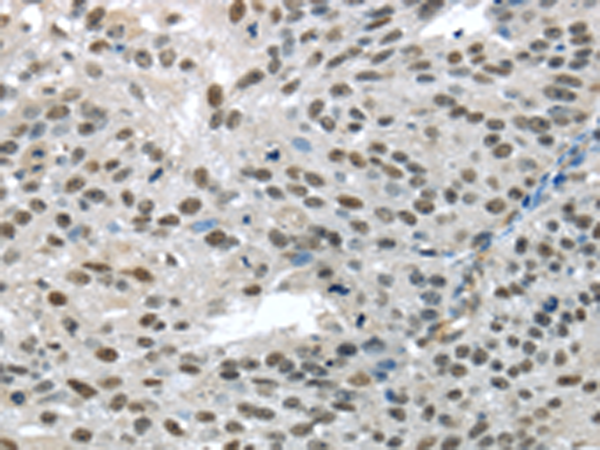
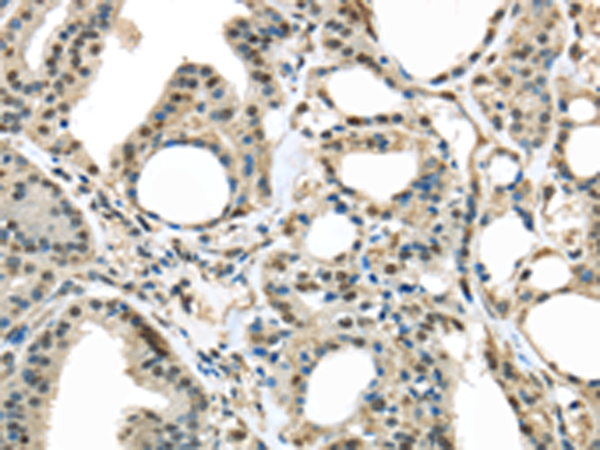
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TK; TKT1; HEL107 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TKT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TKT抗体的示例性参考文献(内容为虚构,仅作格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against Transketolase (TKT) in Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究检测了桥本甲状腺炎患者血清中TKT抗体的表达水平,发现其与疾病活动性呈正相关,提示TKT可能作为自身免疫甲状腺疾病的新型生物标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**:*TKT Antibody as a Diagnostic Marker for Neurological Autoimmunity*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA和免疫印迹法分析,发现TKT抗体在副肿瘤性神经系统综合征患者中特异性升高,表明其可能参与神经细胞损伤的病理机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Mechanistic Role of TKT Autoantibodies in Metabolic Dysregulation*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:实验证实TKT抗体通过抑制转酮醇酶活性干扰磷酸戊糖途径,导致细胞氧化应激增加,为代谢相关自身免疫疾病的治疗提供新靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索真实文献(关键词:Transketolase antibody, TKT autoantibody)。
**Background of TKT Antibodies**
Thiamine kinase (TKT) is an enzyme critical to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), a metabolic route essential for nucleotide synthesis, redox balance, and carbon skeleton production. TKT catalyzes the transfer of a two-carbon ketol group between sugar phosphates, linking glycolysis to PPP and supporting cellular biosynthesis. Dysregulation of TKT activity has been implicated in metabolic disorders, cancer, and diabetic complications, where altered glucose metabolism drives disease progression.
TKT antibodies are immunological tools developed to detect and quantify TKT expression in research and diagnostics. They enable the study of TKT's role in metabolic reprogramming, particularly in cancer cells that rely on PPP for rapid proliferation and antioxidant defense. In diabetes, TKT overexpression has been linked to advanced glycation end product (AGE)-induced pathologies, such as neuropathy and nephropathy.
These antibodies, often monoclonal or polyclonal, are validated for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Recent studies explore TKT as a potential therapeutic target, with inhibitors under investigation for anticancer applications. The development of highly specific TKT antibodies has advanced understanding of metabolic adaptations in disease, highlighting their value in both basic research and translational medicine. Ongoing efforts focus on optimizing antibody sensitivity and cross-reactivity across species to support broader biomedical applications.
×