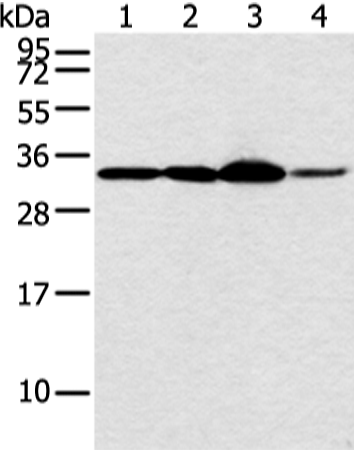
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
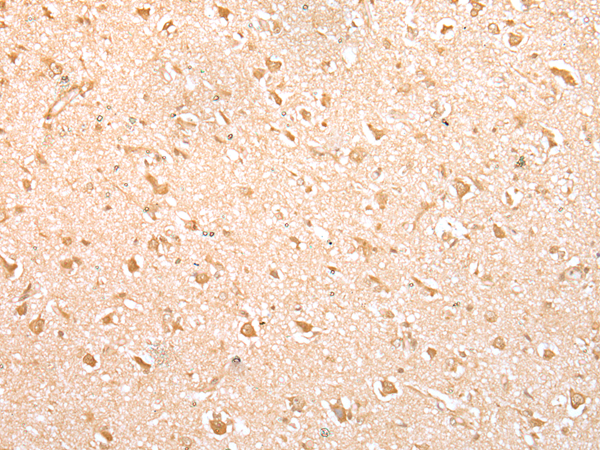
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARC33; NY-REN-28 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MED6抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Structural analysis of the Mediator complex in yeast identifies MED6 as a target for transcriptional regulation"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用MED6特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀和质谱分析,揭示了酵母中介体复合体亚基MED6的结构定位及其在RNA聚合酶II介导的转录起始中的调控作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "MED6 expression profiling in breast cancer using a novel monoclonal antibody"
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种高特异性抗人MED6的单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化证实MED6在乳腺癌组织中的异常高表达,并发现其与患者预后不良显著相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: "The Mediator subunit MED6 is required for embryonic stem cell self-renewal and pluripotency"
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 使用MED6抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP-seq),发现MED6通过调控多能性基因(如Oct4、Nanog)的启动子结合,维持胚胎干细胞的自我更新能力。
---
如需实际文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“MED6 antibody”或“Mediator subunit MED6”获取最新研究。
The MED6 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the Mediator complex, a multi-protein assembly essential for regulating RNA polymerase II (RNAP II)-mediated transcription in eukaryotes. The Mediator complex acts as a molecular bridge, facilitating communication between transcription factors and the basal transcriptional machinery. MED6. a core subunit within the Mediator’s middle module, plays a structural and functional role in stabilizing the complex and modulating its interactions with RNAP II. Research on MED6 has provided insights into transcriptional initiation, elongation, and epigenetic regulation.
Antibodies targeting MED6 are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunofluorescence to investigate its expression, localization, and dynamics under various cellular conditions. Studies employing MED6 antibodies have revealed its involvement in developmental processes, stress responses, and diseases such as cancer, where Mediator subunits are often dysregulated. For example, altered MED6 expression has been linked to tumor progression and drug resistance.
MED6 antibodies also aid in exploring evolutionary conservation, as homologs exist in yeast (Med6) and other model organisms. These tools help dissect Mediator’s architecture and its role in gene-specific or genome-wide regulatory mechanisms. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to the complex’s structural heterogeneity. Overall, MED6 antibodies remain pivotal in advancing our understanding of transcriptional regulation and its implications in health and disease.
×