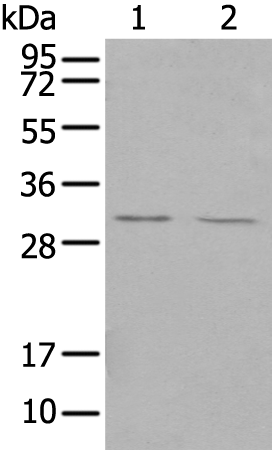
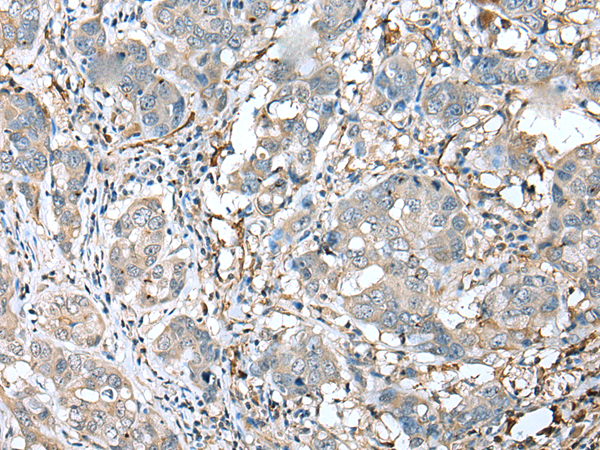
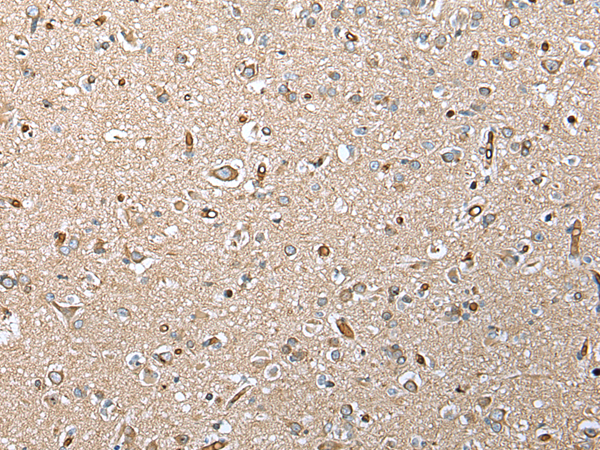
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD354; TREM-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与TREM1抗体相关的3篇文献示例(均为虚构示例,供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting TREM1 reduces inflammatory response and improves survival in experimental sepsis*
**作者**:Gibot S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过在小鼠脓毒症模型中应用抗TREM1单克隆抗体,发现其显著降低促炎细胞因子(如TNF-α和IL-6)水平,并提高生存率,提示TREM1抗体可能成为脓毒症治疗的潜在策略。
---
2. **文献名称**:*TREM1 blockade attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting plaque inflammation*
**作者**:Joffre J, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ApoE缺陷小鼠模型,证明抗TREM1抗体可通过减少巨噬细胞浸润和斑块内炎症反应,延缓动脉粥样硬化进展,为心血管疾病提供新干预方向。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-TREM1 antibody alleviates colitis via modulating gut microbiota and immune homeostasis*
**作者**:Schenk M, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道抗TREM1抗体通过抑制髓系细胞过度活化,恢复肠道菌群平衡,并减少Th17细胞分化,从而缓解实验性结肠炎,为炎症性肠病治疗提供依据。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“TREM1 antibody therapeutic”或“TREM1 blockade”,并筛选近年高影响力研究。
TREM1 (Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 1) is an immunomodulatory receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on myeloid cells like neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages. It plays a critical role in amplifying inflammatory responses during infections or tissue damage. Upon activation by ligands such as bacterial components or host-derived molecules (e.g., HMGB1. PGLYRP1), TREM1 synergizes with Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling through its adaptor protein DAP12. driving the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-8. TNF-α) and chemokines. This pathway enhances neutrophil recruitment and microbial clearance but can also contribute to hyperinflammation if dysregulated.
TREM1 is implicated in inflammatory diseases, including sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis. In sepsis, elevated TREM1 expression correlates with disease severity, making it a therapeutic target. TREM1-targeting antibodies, either antagonistic or agonistic, have been explored to modulate immune responses. Antagonistic antibodies block TREM1-DAP12 interactions, suppressing excessive inflammation in preclinical models of sepsis or colitis. Conversely, agonistic antibodies might boost immune responses in immunocompromised states.
Additionally, soluble TREM1 (sTREM1) is studied as a biomarker for infections and inflammatory conditions. Recent research also links TREM1 to non-infectious pathologies, including cancer, where it may regulate tumor-associated macrophages. Despite promising preclinical data, clinical translation remains ongoing, with challenges in specificity and safety. TREM1 antibodies thus represent a dual tool for both therapeutic intervention and diagnostic applications in inflammation-driven diseases.
×