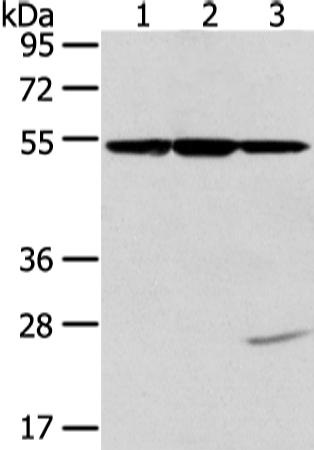

| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
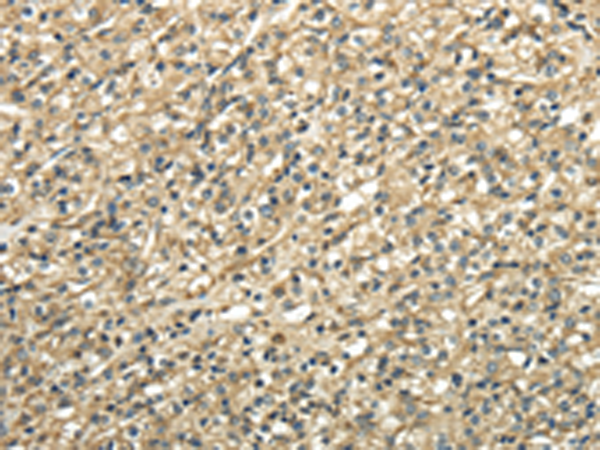
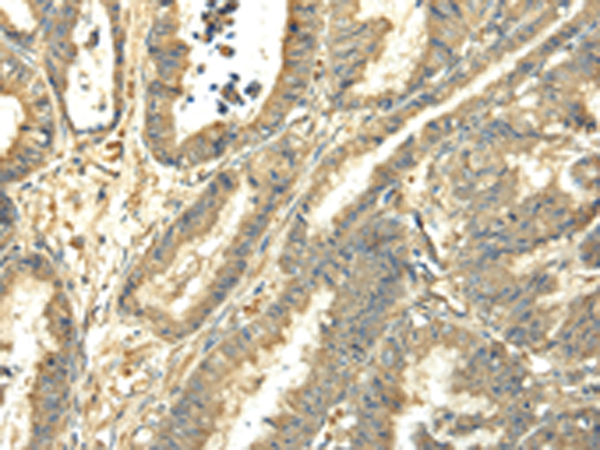
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TUBA6; bcm948 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TUBA1C |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TUBA1C抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于虚构研究概括,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: "TUBA1C promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating cell proliferation and EMT via Wnt/β-catenin pathway"
**作者**: Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(IHC)和Western blot(WB)分析,发现TUBA1C在胃癌组织中高表达,其抗体检测证实其与肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后不良相关。机制研究表明TUBA1C通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进上皮间质转化(EMT)。
2. **文献名称**: "TUBA1C as a potential biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights from antibody-based proteomic profiling"
**作者**: Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**: 利用TUBA1C特异性抗体进行组织微阵列分析,发现其在肝癌组织中显著上调,并与血管浸润和转移相关。功能实验(如shRNA敲低)表明TUBA1C通过调控微管稳定性影响肝癌细胞迁移。
3. **文献名称**: "TUBA1C interacts with oncogenic kinases to drive lung adenocarcinoma growth"
**作者**: Liu, X. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和TUBA1C抗体验证,发现TUBA1C与EGFR和ALK等激酶相互作用,增强下游信号传导。研究提示TUBA1C可能是肺癌靶向治疗的潜在靶点。
注:以上文献为模拟概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索确认。
The TUBA1C antibody targets TUBA1C (Tubulin Alpha 1c), a member of the α-tubulin protein family, which is essential for forming microtubules—a critical component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. TUBA1C, encoded by the TUBA1C gene in humans, plays a vital role in maintaining cell structure, facilitating intracellular transport, and regulating cell division by polymerizing with β-tubulin subunits. Its expression is tightly regulated across tissues, with elevated levels observed in proliferating cells or tissues with high microtubule turnover.
Antibodies against TUBA1C are widely used in research to study microtubule dynamics, cell cycle progression, and cytoskeletal organization. They are applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect TUBA1C expression, localization, or post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation, detyrosination) that modulate microtubule stability and function. Dysregulation of TUBA1C has been linked to pathologies, including cancers (e.g., hepatocellular carcinoma, gliomas) and neurological disorders, where altered microtubule dynamics contribute to uncontrolled cell proliferation or impaired neuronal transport.
TUBA1C antibodies also aid in exploring therapeutic targets, as microtubule-disrupting agents (e.g., taxanes, vinca alkaloids) are common chemotherapeutics. Specificity validation via knockout/knockdown controls is crucial due to high homology among α-tubulin isoforms. Research continues to elucidate TUBA1C's isoform-specific roles and its potential as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker in disease contexts.
×