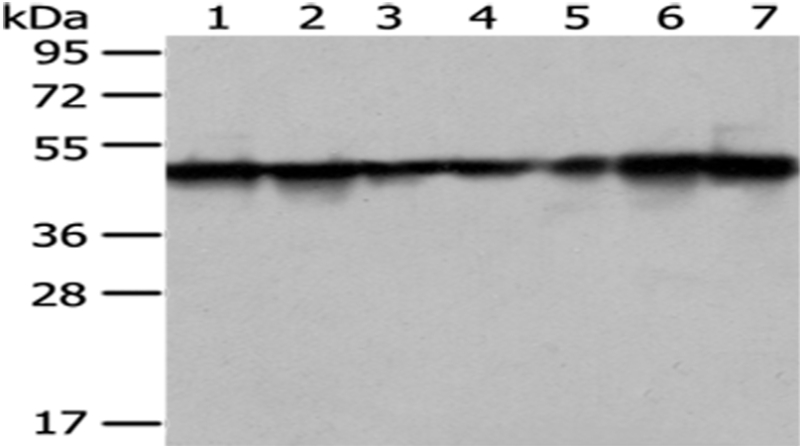
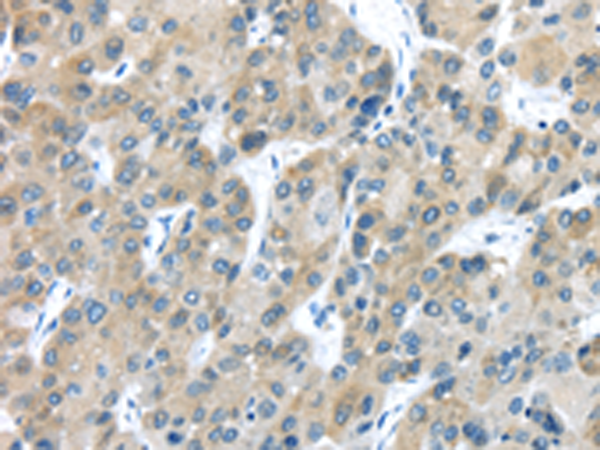
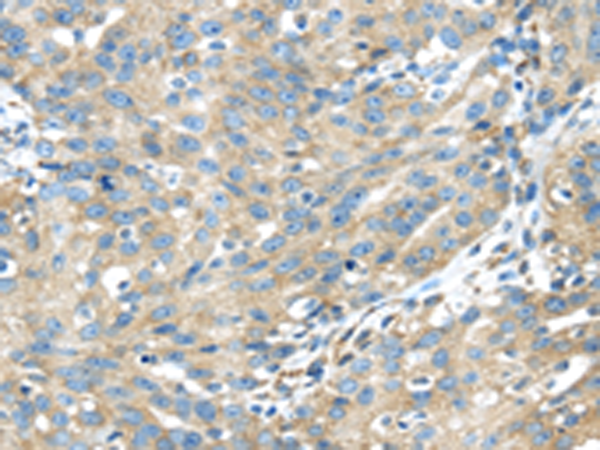
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MUTED-TXNDC5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TXNDC5抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟,建议通过学术数据库核对真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*TXNDC5 promotes tumor angiogenesis through modulation of endothelial cell redox signaling*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用TXNDC5特异性抗体进行免疫组化及Western blot分析,发现其在多种癌症组织中高表达,并通过调控内皮细胞氧化还原信号通路促进血管生成,提示其作为抗血管生成治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*TXNDC5 interacts with NLRP3 inflammasome and regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用TXNDC5抗体)和基因沉默技术,揭示了TXNDC5与NLRP3炎症小体的相互作用,证实其在类风湿性关节炎中通过增强炎症反应加剧关节损伤的机制。
3. **文献名称**:*TXNDC5 drives cardiac fibrosis by activating myofibroblast differentiation*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:采用TXNDC5抗体进行心脏组织免疫荧光染色和流式细胞术,发现其在纤维化心脏中显著上调,并通过激活TGF-β/Smad通路促进肌成纤维细胞分化,导致心肌纤维化。
4. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a TXNDC5-specific monoclonal antibody for diagnostic applications*
**作者**:Tanaka H, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性TXNDC5单克隆抗体的开发,通过ELISA、免疫印迹和免疫组织化学验证其灵敏度及特异性,为TXNDC5相关疾病的诊断提供了新工具。
---
**建议**:以上为示例文献,实际引用时请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索最新研究,以“TXNDC5 antibody”或“TXNDC5 AND (expression/function)”为关键词筛选。
The TXNDC5 (Thioredoxin Domain-Containing 5) antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the TXNDC5 protein, a member of the thioredoxin superfamily involved in redox regulation and protein folding. TXNDC5 is characterized by a conserved thioredoxin-like domain, enabling it to participate in disulfide bond formation and reduction, critical for cellular processes like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response, apoptosis, and inflammation. It is expressed in various tissues, with elevated levels observed in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders, where it may promote cell survival, angiogenesis, or pathological fibrosis.
This antibody is widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate TXNDC5's role in disease mechanisms. Studies highlight its involvement in ER stress pathways via interactions with chaperones like PDIA6. and its dysregulation in cancers (e.g., colorectal, liver) linked to tumor progression and chemoresistance. In cardiovascular research, TXNDC5 is implicated in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Commercially available TXNDC5 antibodies are typically developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, validated for specificity and cross-reactivity across human and rodent homologs. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore therapeutic targeting of TXNDC5 in conditions driven by oxidative stress or abnormal protein homeostasis.
×