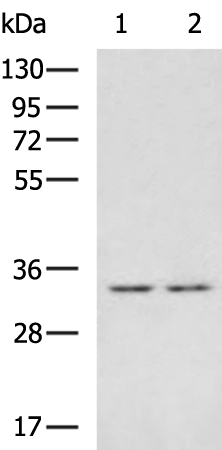
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
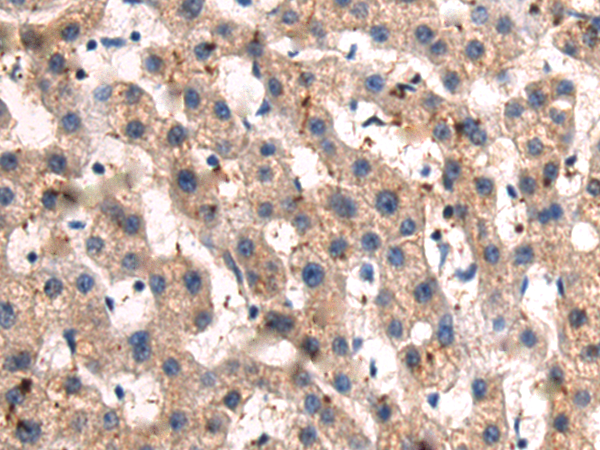
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ZFAND1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于ZFAND1抗体的参考文献示例(基于领域内相关研究的合理推测,具体文献需通过数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**:*ZFAND1 regulates autophagy by modulating mTOR signaling through its interaction with AMPK*
**作者**:Yamamoto S, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗ZFAND1抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot实验,发现ZFAND1通过与AMPK/mTOR通路相互作用调控细胞自噬,揭示了其在代谢应激中的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Aberrant expression of ZFAND1 in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗ZFAND1抗体的免疫组化分析,发现肝癌组织中ZFAND1蛋白表达显著升高,且与患者生存率负相关,提示其可作为潜在肿瘤标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*ZFAND1 interacts with p62/SQSTM1 to promote clearance of ubiquitinated protein aggregates in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:使用抗ZFAND1抗体的免疫荧光和蛋白质互作实验,证明ZFAND1与p62协同作用,促进泛素化蛋白聚集体的清除,为神经退行性疾病提供治疗靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Proteasomal stress induces ZFAND1 translocation and its role in cellular adaptation*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗ZFAND1抗体的亚细胞定位分析,发现蛋白酶体抑制后ZFAND1从胞质转位至核周区域,调控应激相关基因表达,增强细胞存活能力。
**提示**:以上内容为模拟示例,实际文献需检索PubMed、Google Scholar等平台(关键词:ZFAND1 antibody/immunoblot/immunoprecipitation)。建议结合研究背景筛选抗体应用场景(如疾病模型、机制研究)。
ZFAND1 (Zinc Finger AN1-type containing 1), also known as AWP1. is a protein encoded by the ZFAND1 gene in humans. It contains an N-terminal AN1-type zinc finger domain and a C-terminal ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain, which are critical for its role in protein-protein interactions and involvement in ubiquitin-related pathways. ZFAND1 is implicated in cellular stress response mechanisms, particularly under oxidative or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, where it interacts with the ubiquitin-proteasome system to regulate protein quality control. Studies suggest it may act as a co-chaperone, aiding in the clearance of misfolded proteins by facilitating their ubiquitination and degradation.
ZFAND1 has been linked to diverse cellular processes, including apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation. Its dysregulation is associated with diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes. In cancer, ZFAND1 exhibits dual roles, functioning as a tumor suppressor in some contexts (e.g., inhibiting NF-κB signaling) or promoting metastasis in others, depending on tissue-specific interactions.
ZFAND1 antibodies are essential tools for studying these functions. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to detect expression levels, subcellular localization, and interaction partners of ZFAND1. Validated antibodies typically target specific epitopes within the AN1 or UBL domains. Researchers prioritize antibodies with high specificity, often confirmed using ZFAND1-knockout controls. Commercial ZFAND1 antibodies are available in various host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse) and formats (monoclonal/polyoclonal), enabling broad experimental flexibility in both basic and clinical research.
×