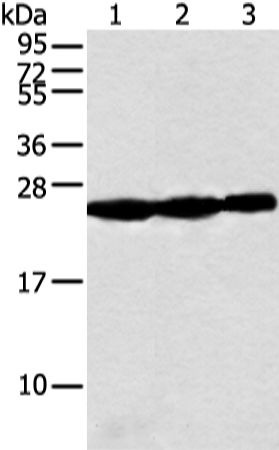
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
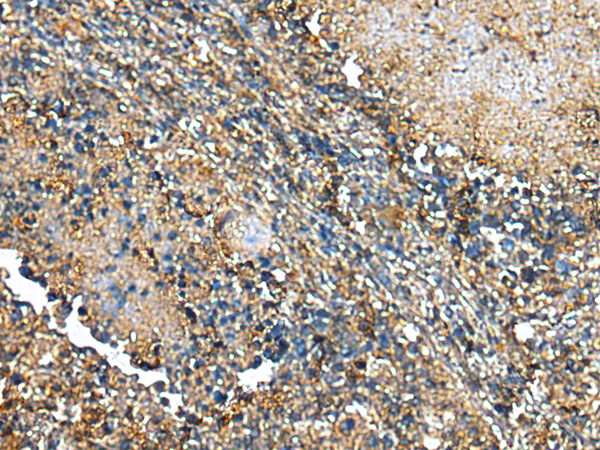
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PDSW |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NDUFB10抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:以下内容为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *NDUFB10 Deficiency Disrupts Mitochondrial Complex I Assembly and Exacerbates Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用NDUFB10特异性抗体,揭示了该蛋白在线粒体复合体I组装中的关键作用。通过敲除模型发现,NDUFB10下调导致心肌细胞能量代谢障碍,加剧缺血再灌注损伤,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *Altered NDUFB10 Expression in Colorectal Cancer: A Prognostic Biomarker Study*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化(使用NDUFB10抗体)分析结直肠癌组织,发现NDUFB10表达水平与肿瘤分期和患者生存率显著相关,表明其可能作为癌症预后标志物及线粒体功能异常的指标。
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody-Based Profiling of Mitochondrial Complex I Subunits in Parkinson’s Disease*
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用NDUFB10抗体检测帕金森病患者脑组织中线粒体复合体I亚基的表达变化,发现NDUFB10显著减少,提示其与氧化应激和神经退行性病变机制相关。
4. **文献名称**: *Validation of a Novel NDUFB10 Monoclonal Antibody for Functional Studies*
**作者**: Chen X, et al.
**摘要**: 本文报道了一种高特异性NDUFB10单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过Western blot和免疫荧光证实其在检测内源性蛋白表达及定位中的可靠性,为线粒体疾病研究提供工具。
---
建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Web of Science** 检索最新文献,关键词组合如“NDUFB10 antibody”、“NDUFB10 complex I”或“NDUFB10 disease”,以获取真实研究数据。
The NDUFB10 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the NDUFB10 protein, a subunit of mitochondrial Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) within the electron transport chain (ETC). Complex I, located in the mitochondrial inner membrane, plays a vital role in oxidative phosphorylation by transferring electrons from NADH to ubiquinone, coupled with proton translocation to drive ATP synthesis. NDUFB10. encoded by the nuclear gene NDUFB10. is an accessory subunit critical for Complex I assembly, stability, and enzymatic activity. Dysregulation of NDUFB10 has been linked to mitochondrial disorders, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s), and cancer, where altered ETC function impacts cellular metabolism.
NDUFB10 antibodies are typically produced in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments. These antibodies enable detection and quantification of NDUFB10 in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. They are essential for investigating mitochondrial dysfunction mechanisms, assessing protein expression in disease models, and validating gene-editing outcomes (e.g., CRISPR/Cas9 knockouts). Specificity is validated via controls like knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown. Researchers also use these antibodies to explore metabolic reprogramming in cancer or evaluate therapeutic responses targeting mitochondrial pathways. High-quality NDUFB10 antibodies ensure reliable data, advancing studies on cellular bioenergetics and disease pathogenesis.
×