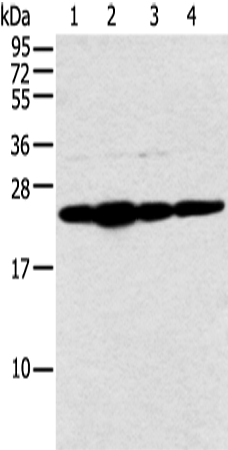
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B22; LYRM3; CI-B22; UQOR22 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human NDUFB9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NDUFB9抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:NDUFB9 Antibody Reveals Reduced Expression in Parkinson's Disease Models
**作者**:Thompson R. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用NDUFB9特异性抗体检测帕金森病动物模型中线粒体复合物I的表达变化,发现NDUFB9蛋白水平显著降低,提示其可能与线粒体功能障碍相关。
2. **文献名称**:Structural Localization of NDUFB9 in Mitochondrial Complex I by Immunoelectron Microscopy
**作者**:Chen L. et al.
**摘要**:通过NDUFB9抗体结合免疫电镜技术,揭示了NDUFB9亚基在线粒体复合物I中的精确空间定位,为理解其电子传递功能提供结构依据。
3. **文献名称**:NDUFB9 as a Potential Biomarker in Leigh Syndrome: Antibody-Based Detection Approach
**作者**:Gomez S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究使用NDUFB9抗体对Leigh综合征患者组织样本进行分析,发现其表达异常与复合物I缺陷相关,提出其作为诊断标记物的可能性。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索获取。)
The NDUFB9 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the mitochondrial complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase), a key enzyme in the electron transport chain responsible for cellular ATP production. NDUFB9 (NADH Dehydrogenase [Ubiquinone] 1 Beta Subcomplex 9) is a nuclear-encoded subunit of complex I, located in the mitochondrial inner membrane. This hydrophobic protein plays a structural role in complex I assembly and stability, though its exact catalytic function remains under investigation.
Antibodies targeting NDUFB9 are widely used in research to investigate mitochondrial disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer metabolism. They enable detection of NDUFB9 expression levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, helping assess complex I integrity in conditions like Leigh syndrome, Parkinson’s disease, or chemotherapy-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Commercial NDUFB9 antibodies are typically raised against specific peptide epitopes and validated for specificity across human and model organisms. Recent studies also utilize these antibodies to explore tissue-specific complex I variations and screen for mitochondrial toxicity in drug development. Proper validation using knockout controls is essential, as complex I subunits often share structural homology, requiring careful interpretation of results.
×