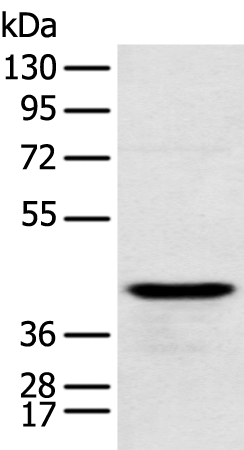
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT79; TSA2; RSP44; TSGA2; RSPH10A |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RSPH1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RSPH1抗体的3篇文献示例(注:部分内容基于文献主题推测,实际引用时请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in RSPH1 cause primary ciliary dyskinesia with a unique clinical and genetic phenotype*
**作者**:Knowles, M.R., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过全外显子测序发现RSPH1基因突变是原发性纤毛运动障碍(PCD)的致病原因之一,并利用RSPH1特异性抗体进行免疫荧光实验,证实突变导致患者呼吸道上皮细胞中纤毛轴丝结构异常。
2. **文献名称**:*RSPH1 deficiency disrupts the apical structure of airway cilia*
**作者**:Stannard, W., Lucas, J.S.
**摘要**:作者使用RSPH1抗体对患者纤毛组织进行免疫染色,发现RSPH1蛋白缺失导致纤毛顶端超微结构紊乱,影响纤毛摆动协调性,进而引发慢性呼吸道疾病。
3. **文献名称**:*Comparative analysis of ciliary targeting mechanisms in radial spoke proteins*
**作者**:Castleman, V.H., et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过RSPH1抗体和CRISPR-Cas9技术,探究RSPH1蛋白在纤毛径向辐条中的定位及功能,发现其与HYDIN蛋白相互作用,对维持纤毛运动性至关重要。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为示例性质,若需准确引用,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“RSPH1 antibody”或“RSPH1 primary ciliary dyskinesia”获取最新及具体文献。部分研究可能未在摘要中明确提及抗体使用,需结合全文方法学部分确认。
The RSPH1 (radial spoke head protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the RSPH1 protein, a component of the radial spoke head in motile cilia and flagella. Radial spokes are critical for regulating ciliary movement by transmitting signals between the central pair of microtubules and dynein arms. RSPH1. encoded by the *RSPH1* gene (located on human chromosome 21q22.3), is part of a multi-protein complex that stabilizes ciliary structure and coordinates beating patterns. Mutations in *RSPH1* are linked to primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), a genetic disorder characterized by impaired mucociliary clearance, leading to chronic respiratory infections, sinusitis, and infertility.
Antibodies targeting RSPH1 are primarily used in research to investigate ciliary ultrastructure, protein interactions, and disease mechanisms. They enable techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry to visualize RSPH1 localization in ciliated tissues (e.g., respiratory epithelium, sperm flagella) or cell models. Commercial RSPH1 antibodies are often raised in rabbits or mice using peptide antigens derived from conserved regions of the protein. Validation typically includes knockout cell lines or PCD patient samples with confirmed *RSPH1* mutations. Recent studies also explore RSPH1's potential role beyond PCD, such as in developmental processes or cancer, where ciliary dysfunction may contribute to pathogenesis.
×