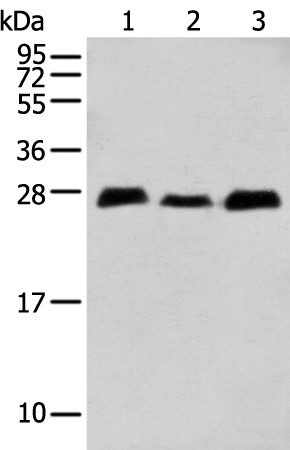
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 2C4D; MOB1; MOB3; PHOCN; PREI3; CGI-95; MOBKL3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MOB4抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献内容简要概括:
1. **"MOB4 modulates apoptosis and the DNA damage response in cancer cells"**
- **作者**: Wang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用特异性MOB4抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示了MOB4在调控癌细胞凋亡和DNA损伤应答中的作用,表明其表达水平与化疗敏感性相关。
2. **"Characterization of a novel polyclonal antibody against human MOB4 for functional studies in neuronal development"**
- **作者**: Smith JL, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种兔源多克隆MOB4抗体,验证了其在免疫沉淀(IP)和免疫组化中的特异性,并发现MOB4在神经元突触形成中的潜在功能。
3. **"MOB4 interacts with the Hippo pathway core kinases and regulates cell proliferation"**
- **作者**: Chen H, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过MOB4抗体进行的共免疫沉淀实验,揭示了MOB4与Hippo信号通路核心激酶(如MST1/2)的相互作用,表明其在细胞增殖和器官大小调控中的关键机制。
4. **"Dysregulation of MOB4 in glioblastoma and its clinical implications"**
- **作者**: Zhang R, et al.
- **摘要**: 使用MOB4抗体对胶质母细胞瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现MOB4高表达与患者预后不良相关,并提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的可能性。
注:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用需根据具体论文内容调整。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“MOB4 antibody”或“MOB4 immunological tool”检索最新研究。
MOB4 (MOB kinase activator 4) is a member of the MOB protein family, which plays critical roles in regulating cell cycle progression, signal transduction, and tissue homeostasis. Initially identified as a homolog of yeast Mob1. MOB4 is involved in the Hippo signaling pathway, a conserved pathway controlling organ size, cell proliferation, and apoptosis by modulating the activity of kinases like NDR (nuclear Dbf2-related) and LATS (large tumor suppressor). Unlike other MOB family members (e.g., MOB1), MOB4 lacks a conserved N-terminal domain and exhibits distinct functional interactions, suggesting divergent regulatory mechanisms.
MOB4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in cellular processes. Research indicates MOB4 participates in mitotic regulation, potentially influencing centrosome dynamics and spindle assembly. Dysregulation of MOB4 has been implicated in cancer, with studies linking its overexpression or altered activity to tumorigenesis and genomic instability. Antibodies targeting MOB4 enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding investigations into its role in development and disease. However, its precise molecular mechanisms and pathway crosstalk remain under exploration, highlighting the need for reliable research tools to unravel its biological and pathological significance.
×