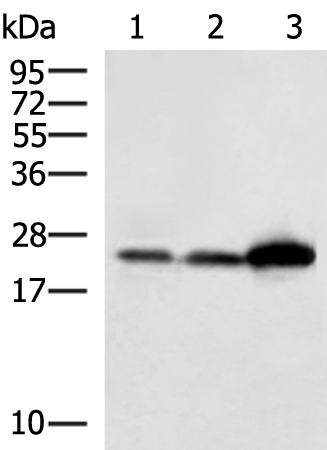
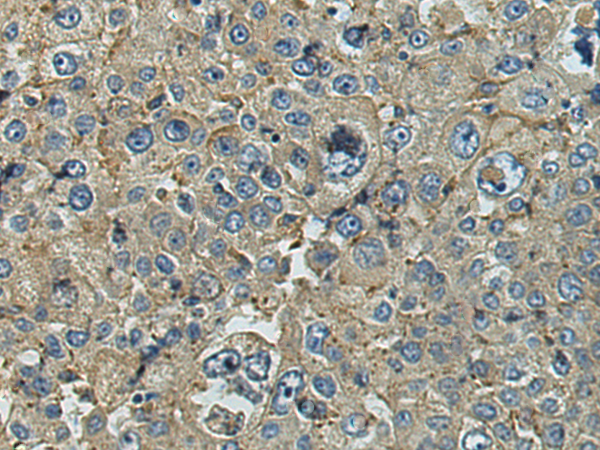
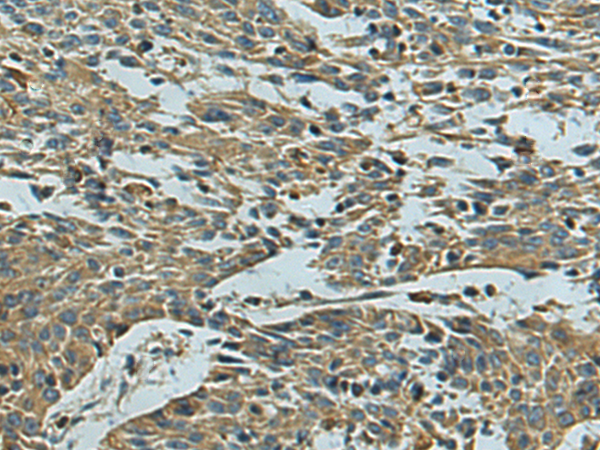
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VMA4; ATP6E1; ATP6EL2; ATP6V1EL2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ATP6V1E2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATP6V1E2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容可能为虚构或示例性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1E2 mutations impair V-ATPase function in autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过基因测序发现ATP6V1E2基因突变导致V-ATP酶功能缺陷,引发肾小管酸中毒。利用ATP6V1E2特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实突变降低了该亚基在肾细胞中的表达和定位。
2. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1E2 overexpression promotes extracellular matrix degradation in prostate cancer metastasis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:作者发现前列腺癌细胞中ATP6V1E2表达上调,通过抗体介导的免疫组化分析,证实其高表达与溶酶体活性增强相关,促进肿瘤微环境ECM降解,从而加速癌症转移。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting ATP6V1E2 for lysosomal pH monitoring*
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高特异性ATP6V1E2单克隆抗体,通过流式细胞术和共聚焦显微镜验证其在检测溶酶体V-ATP酶组装及pH调节中的应用,为溶酶体功能障碍疾病提供新工具。
**提示**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar或Web of Science等平台检索确认。若研究主题较新,建议扩大关键词范围(如V-ATPase E2亚基、溶酶体酸化的分子机制等)。
The ATP6V1E2 antibody targets the ATP6V1E2 protein, a subunit of the vacuolar-type H+-translocating ATPase (V-ATPase) complex, which plays a critical role in regulating intracellular pH and membrane trafficking. V-ATPases are multisubunit proton pumps that acidify organelles like lysosomes, endosomes, and secretory vesicles, influencing processes such as protein degradation, ion homeostasis, and neurotransmitter release. The ATP6V1E2 subunit, part of the V1 domain, is involved in ATP hydrolysis and proton translocation. While the ubiquitously expressed ATP6V1E1 is well-characterized, ATP6V1E2 is a less-studied isoform with tissue-specific expression, notably in the kidney, testis, and certain cancer cells.
Antibodies against ATP6V1E2 are primarily used in research to investigate its physiological roles and dysregulation in diseases. Studies suggest ATP6V1E2 may contribute to renal tubular acidosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and tumor progression, where altered V-ATPase activity affects microenvironment acidity and cell survival. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in protein localization and expression analysis. Commercial ATP6V1E2 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for specificity using knockout controls. Their development supports ongoing exploration of V-ATPase diversity and isoform-specific functions, offering insights into therapeutic targeting for conditions linked to pH dysregulation.
×